Robotics in Logistics: Top Trends & Automation Innovations
As global trade accelerates and consumer expectations for faster delivery continue to rise, logistics companies are under increasing pressure to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance accuracy. Robotics and automation have emerged as powerful solutions to these challenges, ushering in a new era of intelligent, efficient supply chain management.
This article explores the latest trends and innovations in robotics and automation within the logistics sector, along with their real-world applications, benefits, and future potential.
1. The Growing Role of Robotics in Modern Logistics

Logistics operations, particularly in warehousing and fulfillment, are heavily reliant on speed and precision. Robotics has significantly altered how these tasks are handled.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are now commonly used for transporting goods within warehouses. Unlike traditional conveyor systems, these robots are flexible, scalable, and capable of navigating complex layouts using sensors and maps.
Robotic arms are deployed for picking, palletizing, and packaging tasks. These machines, once exclusive to manufacturing, now play a central role in warehouse logistics.
Companies like Amazon, JD.com, and DHL have integrated large fleets of robots in their fulfillment centers. Amazon’s Kiva robots, for example, move entire shelving units to human pickers, drastically reducing the time spent walking and increasing order fulfillment efficiency.
2. Automated Warehousing: Smarter, Faster, More Efficient
Warehousing is the backbone of logistics, and automation is redefining what’s possible in this domain.
Key innovations include:
- Goods-to-person (G2P) systems: Robots bring products directly to human operators, minimizing movement and fatigue.
- High-density automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS): These vertical systems utilize robotic cranes to retrieve inventory from tall racks, saving floor space and speeding up storage processes.
- AI-powered inventory tracking: Using computer vision and RFID technology, automated systems can track inventory in real time, improving accuracy and reducing shrinkage.
The result is a warehouse that can operate 24/7, manage thousands of SKUs, and scale seamlessly during peak periods.
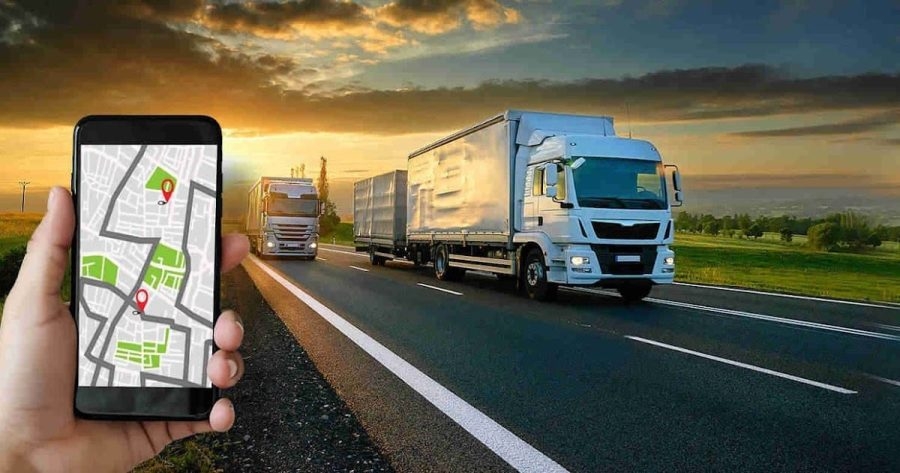
3. Innovations in Last-Mile Delivery: Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
The most complex and costly part of logistics is often the “last mile”—getting a product from the local distribution hub to the customer’s door. Robotics is transforming this space through:
- Delivery drones: Companies like Zipline and Wing are already using drones for rapid delivery of medical supplies, groceries, and small packages in remote or high-demand areas.
- Autonomous delivery vehicles: Self-driving vans and sidewalk delivery robots (e.g., Starship Technologies) are being tested in urban environments to reduce delivery times and labor costs.
- Smart lockers and robotic pickup stations: These reduce delivery attempts and allow customers to retrieve parcels at their convenience, enhancing the delivery experience.
While regulatory hurdles remain, the development of autonomous delivery technology is advancing rapidly.
4. Artificial Intelligence as the Brain Behind Automation

While robots perform physical tasks, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the strategic mind behind the operations.
AI in logistics enables:
- Predictive analytics: Forecasting demand, warehouse stock levels, and delivery times with greater accuracy.
- Dynamic route optimization: AI can recalculate delivery routes in real time based on traffic, weather, or delays.
- Automated decision-making: Whether determining reorder points or selecting shipping carriers, AI reduces human intervention and speeds up processes.
AI and robotics together form a self-learning, adaptive logistics ecosystem capable of responding to real-world complexity with minimal human oversight.
5. Human-Robot Collaboration: The Rise of Cobots
Contrary to the fear that robots will replace human jobs, many logistics firms are deploying collaborative robots (cobots) designed to work alongside human workers.
Cobots handle repetitive or physically demanding tasks such as heavy lifting or sorting.
Human workers supervise complex decision-making, quality control, and customer-facing interactions.
This synergy leads to increased safety, reduced injury rates, and higher employee satisfaction. In fact, cobots are helping address labor shortages in many regions where warehouse staffing is difficult or costly.
6. Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, the implementation of robotics and automation is not without challenges:
- High initial investment: Procuring and installing automation systems involves significant capital, which can be a barrier for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Integration complexity: Aligning new technologies with legacy systems, existing workflows, and IT infrastructure requires careful planning.
- Cybersecurity risks: As systems become more connected, protecting them from cyberattacks is essential.
- Workforce transition: Companies must invest in training employees to work with and maintain automated systems, ensuring a smooth shift to a hybrid human-machine environment.
Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic, phased approach to automation—starting with high-impact areas and scaling progressively.
7. The Road Ahead: What the Future Holds

The future of logistics is undoubtedly automated, intelligent, and autonomous.
Upcoming trends to watch include:
- 5G-powered robotics: Ultra-fast, low-latency communication will enable real-time coordination of robots across vast networks.
- Digital twins: Virtual replicas of logistics operations will allow for simulation, optimization, and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainable automation: Robotics will play a key role in reducing waste, emissions, and energy usage in supply chain operations.
As the industry evolves, logistics providers that adopt these technologies early will gain a significant competitive advantage, ensuring faster delivery, higher customer satisfaction, and more resilient supply chains.
Conclusion
Robotics and automation are no longer futuristic concepts—they are foundational pillars of modern logistics. From warehouse operations to last-mile delivery, these technologies are transforming the way goods are stored, moved, and delivered. While challenges remain, the pace of innovation and the tangible benefits of automation ensure that its role in logistics will only continue to grow. Businesses that embrace this transformation will lead the way in building the next generation of supply chains.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua








[…] Understanding Big Data in the Logistics […]