Innovations in Last Mile Delivery for E-commerce
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, the last mile — the final leg of a product’s journey from warehouse to customer — has become both a critical differentiator and a major logistical challenge. As customer expectations for speed, transparency, and convenience continue to rise, businesses are turning to innovative last mile delivery solutions to stay competitive. This article explores the most transformative trends reshaping last mile logistics and their implications for the future of e-commerce.

I. The Growing Pressure on Last Mile Delivery
The surge in online shopping, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and changing consumer habits, has put immense pressure on delivery infrastructure. Customers now demand same-day or even two-hour delivery windows, forcing retailers and logistics providers to rethink traditional delivery models. Last mile delivery often accounts for more than 50% of the total shipping cost, making it not only a customer satisfaction issue but also a financial one.
II. Key Innovations in Last Mile Logistics

1. Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Micro-fulfillment centers are small-scale warehouses strategically located near urban populations. These centers store high-demand items and enable faster, localized delivery. Retailers like Walmart and Amazon have embraced MFCs to bring inventory closer to the consumer, reducing delivery time and cost.
2. Crowdsourced Delivery Networks
Companies like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Postmates have extended their gig-economy model to retail deliveries. Crowdsourced delivery platforms connect freelance drivers with businesses needing flexible, on-demand last mile logistics. This model enables hyper-local delivery with minimal overhead.
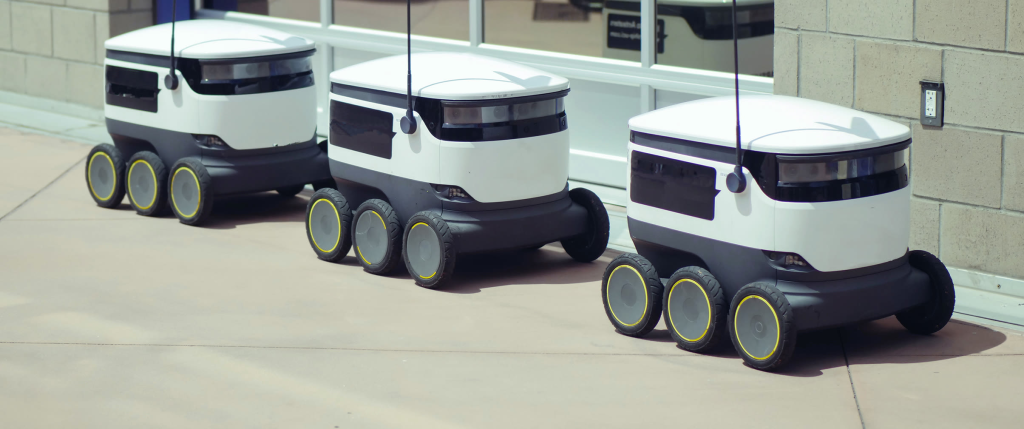
3. Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
Robotics and automation are reshaping urban delivery. Autonomous ground vehicles (AGVs), drones, and delivery robots are being piloted to eliminate human labor, reduce errors, and operate around the clock. For example, Starship Technologies has deployed delivery robots on college campuses and within neighborhoods.
4. Smart Lockers and Pickup Points

Instead of delivering to a customer’s door, smart lockers and designated pickup points offer more secure and efficient alternatives. Amazon Locker and similar services allow customers to retrieve packages at their convenience, reducing failed deliveries and package theft.
5. Route Optimization with AI and Machine Learning
AI-powered logistics platforms help delivery companies optimize routes in real-time, accounting for traffic, weather, customer availability, and vehicle capacity. This not only improves delivery speed but also lowers fuel consumption and emissions.
6. Sustainable Delivery Methods
Sustainability is gaining traction in last mile logistics. Electric bikes and vans, consolidated delivery windows, and carbon offset initiatives are being adopted to reduce the environmental impact. Companies like DHL and UPS are investing heavily in electric fleets and green logistics infrastructure.
III. Benefits of Last Mile Innovation

Innovations in last mile delivery bring several benefits:
- Faster delivery times, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost reduction through automation, better route planning, and decentralized fulfillment.
- Improved transparency, with real-time tracking and predictive delivery updates.
- Greater scalability for retailers expanding into new markets or high-density urban areas.
IV. Challenges and Considerations
Despite technological advances, several challenges persist:
- High implementation costs for automation and infrastructure.
- Regulatory hurdles around drone flights and autonomous vehicle use.
- Logistical complexity in managing returns, failed deliveries, and peak season demand.
- Workforce transition, as gig workers and AI replace traditional roles.
V. The Future of Last Mile Delivery

The future of last mile logistics lies in a hybrid model that combines technology, human flexibility, and sustainability. We can expect increased adoption of AI-driven decision-making, personalized delivery options, and deeper integration between e-commerce platforms and logistics networks. As competition intensifies, the last mile will increasingly be the battleground for customer experience and brand loyalty.
Conclusion
Last mile delivery is no longer just the final step in order fulfillment — it is the front line of customer engagement. Retailers that invest in innovative last mile solutions are better equipped to meet modern consumer demands and operate efficiently in a highly competitive landscape. As technology continues to evolve, the last mile will become faster, smarter, and more sustainable than ever before.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua