Tracking Innovations in Global Logistics: From Manual to Automated Shipment Tracking
Shipment tracking has undergone one of the biggest transformations in the logistics industry. What once depended on phone calls, paperwork, and guesswork has evolved into a fast, automated, and transparent system driven by technology. Today’s businesses and customers expect accurate, real-time visibility—and automation is now the most reliable method to deliver it.
This expanded guide explains how shipment tracking has changed over time, what technologies matter today, and why automated systems are becoming essential for any modern supply chain.
1. Manual Tracking: Slow, Unreliable, and Labor-Intensive
1.1 How Manual Tracking Worked
Before digital tools existed, logistics teams relied heavily on manual processes. Each step required effort, coordination, and time:
- Staff had to call drivers, couriers, or warehouses multiple times a day to ask for shipment updates
- Paper logs recorded arrival and departure times, making it difficult to track changes
- Spreadsheets became outdated within hours
- Customers often waited days for status updates
- Information was frequently missing, unclear, or inconsistent
Without real-time visibility, teams struggled to predict delays or solve problems early. Miscommunication between departments was common, leading to frustrated customers and higher operational costs.
1.2 Why Manual Tracking Caused Major Problems
Manual tracking increased the risk of:
- Human error during data entry
- Lost shipment records
- Delayed issue detection
- Poor customer experience
- Limited ability to scale operations
This process worked decades ago, but today’s fast-paced logistics environment demands faster, more accurate solutions.
2. First Digital Solutions: A Step Forward
2.1 Early Digital Tools
With the rise of basic digital systems, the logistics industry took an important step forward. Common tools included:
- Barcode scanners at departure, transit, and arrival points
- Courier websites offering basic shipment status
- Automatically generated email notifications

- Web dashboards that provided simple tracking timelines
These systems helped reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and speed up communication.
2.2 Limitations of Early Digital Tracking
Despite these improvements, visibility was still limited:
- Tracking updates were not always real-time
- Different carriers used separate platforms
- Shipment data was often incomplete
- Customers still experienced uncertainty
- Internal teams lacked unified access to information
These early systems improved efficiency—but were not enough to support global or complex supply chains.
3. Full Automation and Real-Time Visibility
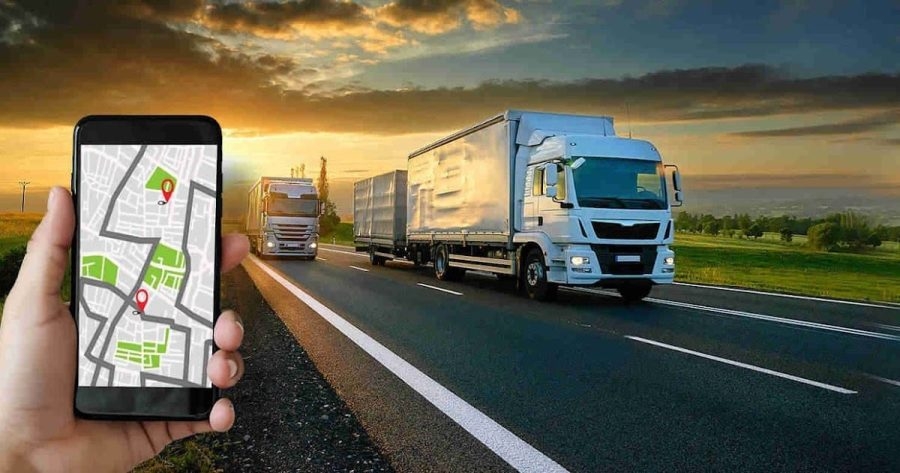
3.1 GPS Tracking and Live Location Updates
GPS technology revolutionized shipment tracking. Modern systems allow:
- Continuous live location streaming
- Route monitoring
- Accurate delivery time predictions
- Instant alerts when delays occur
This level of visibility helps businesses adjust schedules quickly and provide accurate delivery updates to customers.
3.2 IoT Monitoring for Sensitive Goods
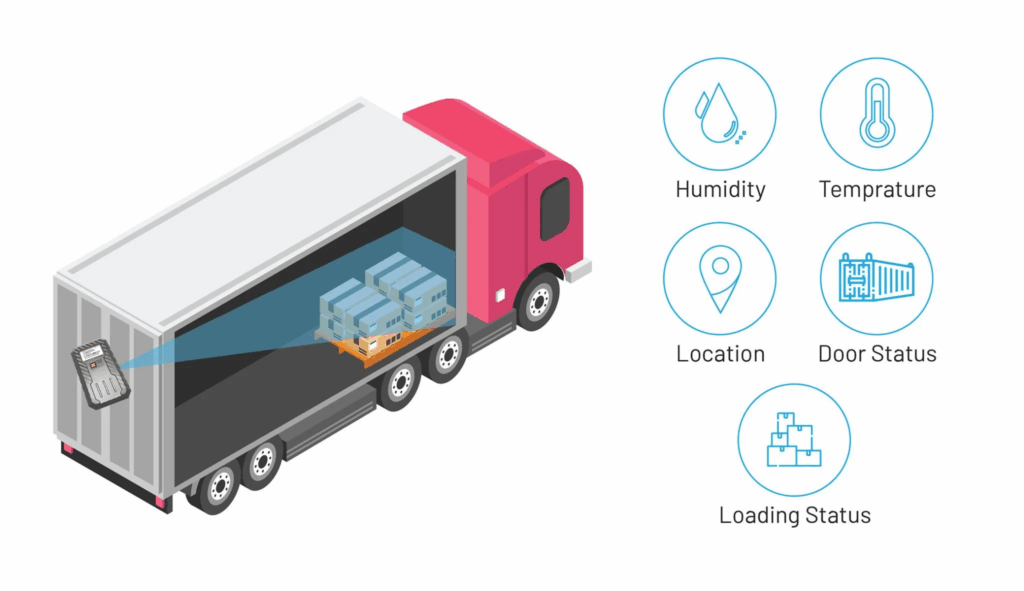
IoT devices add another layer of intelligence. These sensors track:
- Temperature changes
- Humidity levels
- Sudden impacts
- Light exposure
- Vibration patterns
Industries like healthcare, food delivery, cosmetics, and electronics benefit from this data. When conditions fall outside the acceptable range, the system sends automatic alerts, allowing rapid intervention before damage occurs.
3.3 Predictive Analytics Powered by AI
AI improves shipment tracking by forecasting risks and optimizing performance. Predictive analytics can:
- Estimate delays caused by weather or customs
- Suggest faster routes
- Predict arrival times more accurately
- Identify patterns that cause recurring issues
- Help companies select the most reliable carriers
This leads to better planning, fewer delays, and smoother global transportation.
3.4 Cloud-Based Tracking Platforms
Unlike early systems, modern cloud platforms connect the entire supply chain. These platforms:
- Centralize all tracking data
- Sync with warehouse management systems
- Integrate with ERP and transportation management software
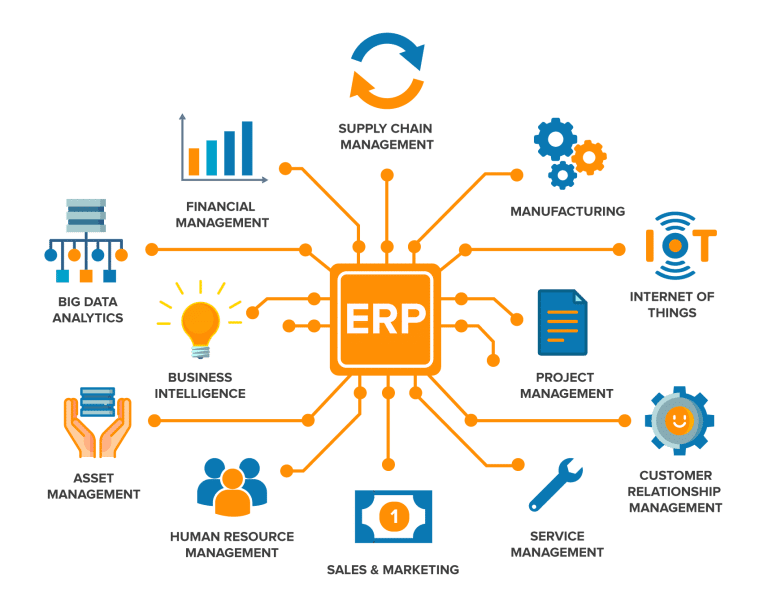
- Provide real-time dashboards for teams and customers
- Allow global access from any device
This unified visibility ensures everyone—from warehouse workers to end customers—views the same updated information at the same time.
4. What Businesses Gain from Automated Shipment Tracking
4.1 Faster and More Efficient Operations
Automation eliminates repetitive tasks:
- No more manual status requests
- Automatic alerts reduce monitoring time
- Issues are identified early, minimizing disruption
Teams can focus on problem-solving instead of administrative work.
4.2 Improved Customer Satisfaction
Customers value transparency. Automated tracking provides:
- Real-time tracking links
- Timely notifications
- Predictable delivery experiences
- Higher trust in the brand

This reduces customer service inquiries and increases satisfaction.
4.3 Smarter Decision-Making for Logistics Teams
With accurate data, companies can make better decisions:
- Evaluate carrier performance
- Optimize delivery routes
- Lower fuel and labor costs
- Improve warehouse scheduling
Automation creates a more strategic and data-driven supply chain.
4.4 Enhanced Safety for Shipments
Sensitive shipments are protected through:
- Temperature monitoring
- Impact detection
- Real-time condition alerts
This greatly reduces the risk of product damage or loss.
5. One System Connecting Many Players
5.1 Multi-Party Visibility
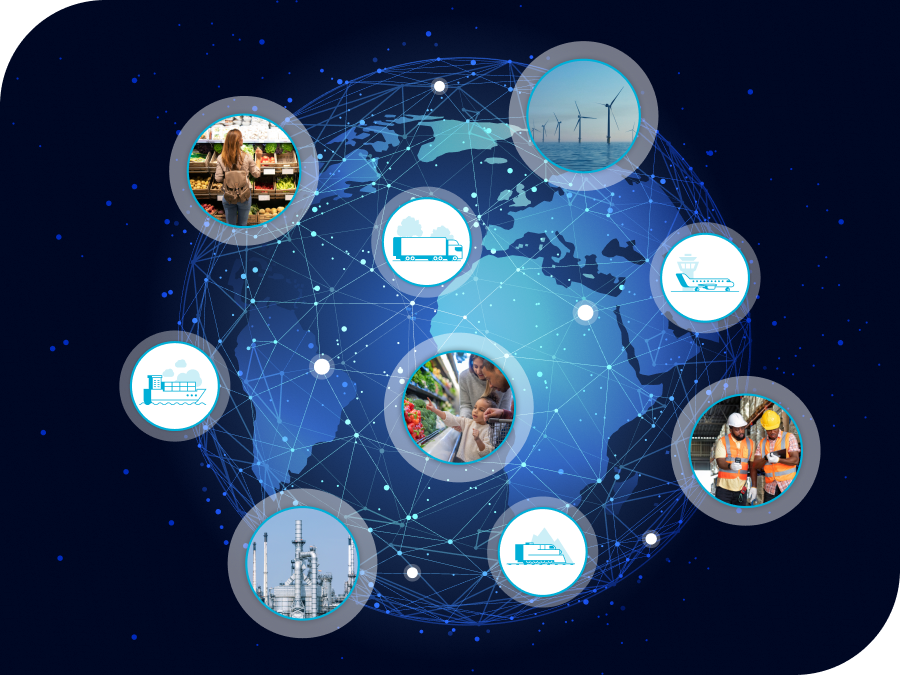

Automated shipment tracking benefits everyone involved:
- Transport companies can plan routes efficiently
- Freight forwarders gain visibility across multiple carriers
- Warehouses receive accurate ETA information
- Customs brokers access shipment details faster
- Distribution centers prepare for incoming loads
- End customers track their parcels in real time
Because all data is synchronized, communication becomes faster and mistakes are significantly reduced.
6. Common Barriers to Full Visibility
6.1 Fragmented Tracking Systems Across Regions
Different carriers often use different technologies, which can lead to scattered data. Modern platforms solve this with:
- Multi-carrier compatibility
- API integrations
- Unified dashboards
This ensures smooth data flow regardless of region or carrier.
6.2 High Initial Investment

Some teams view automation tools as expensive. Yet businesses soon discover:
- Reduced labor costs
- Fewer shipment errors
- Improved delivery speed
- Better customer retention
Over time, automation pays for itself.
6.3 Staff Resistance to New Tools
Introducing new technology can feel overwhelming. Proper onboarding is essential:
- Provide training
- Demonstrate time savings
- Highlight accuracy and cost benefits
Once employees see how much easier their work becomes, adoption improves quickly.
7. What’s Next in Shipment Tracking Innovation
7.1 The Future of Tracking Technology
Shipment tracking will continue evolving. Future innovations include:
- Blockchain for secure, tamper-proof tracking records
- More advanced AI route optimization
- Cross-platform dashboards connecting all carriers and partners
- Environmental impact tracking to measure carbon footprint
- Fully automated customs workflows
- Drone-assisted scanning and delivery visibility
These advancements aim to improve global logistics with greater transparency, speed, and sustainability.
Conclusion
Shipment tracking has progressed from handwritten logs to real-time dashboards supported by AI and IoT technology. Businesses that embrace automated tracking can solve problems earlier, operate more efficiently, and offer customers a smoother experience.
Today, reliable shipment tracking is not just a convenience—it is a critical foundation for modern logistics, global trade, and customer satisfaction. Companies that invest in automation will gain a competitive advantage and build stronger partnerships across the entire supply chain.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua








[…] code assigned to your shipment when booked. Think of it as your package’s ID card. Carriers, logistics companies, and customers use them to monitor the movement of goods from origin to […]