Challenges of International Shipment Tracking in Remote Regions
International Shipment Tracking has become a vital part of global logistics. Businesses and customers rely on accurate updates to know where their goods are and when they will arrive. While tracking works smoothly in developed regions, the story is very different in remote areas. Harsh geography, weak infrastructure, and limited connectivity make tracking goods far more complicated. Understanding these challenges helps companies find better solutions and keep customer trust.

Why Is Tracking More Difficult in Remote Regions?
What Defines a Remote Region?
Remote regions include rural villages, mountainous areas, deserts, and isolated islands. These areas often lack the infrastructure that urban centers take for granted. Roads may be unpaved, electricity may be unreliable, and internet connections are weak or absent.
Why Does It Matter for Tracking?
International Shipment Tracking depends on three things: data accuracy, timely updates, and reliable communication networks. Remote regions often fail to provide one or more of these. The result is tracking updates that are late, missing, or misleading, frustrating both sellers and buyers.
What Are the Main Infrastructure Barriers?
Poor Transportation Networks
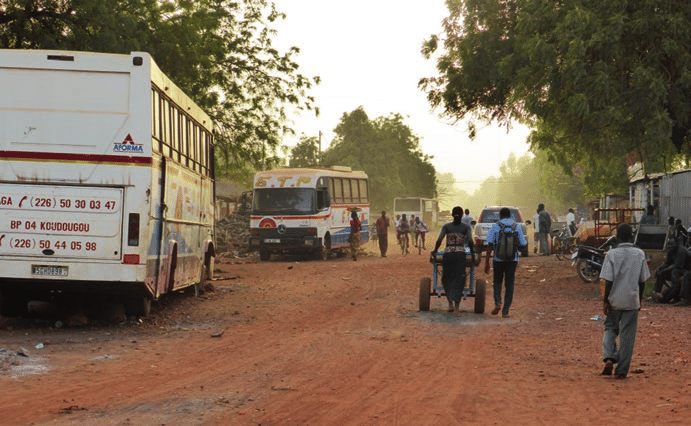

- Unpaved or damaged roads slow down shipments.
- Seasonal conditions like floods or snowstorms make transport routes inaccessible.
- Delivery vehicles may rely on manual transport such as motorcycles, donkeys, or boats, which are harder to integrate with tracking systems.
Limited Energy Supply
Shipment tracking devices require power. In remote regions, electricity can be unstable or unavailable. This makes it difficult to keep scanners, GPS devices, and communication tools active at all times.
Weak Internet and Mobile Coverage
International Shipment Tracking depends heavily on internet and mobile networks. In remote zones:
- Tracking scans may not upload in real time.
- Updates appear only after the package reaches an area with better coverage.
- Customers see long gaps in their tracking history, creating uncertainty.
How Do Environmental Factors Complicate Tracking?
Harsh Weather Conditions

Extreme climates such as deserts, rainforests, or mountain ranges make logistics unpredictable. Devices may fail due to heat, moisture, or cold. Shipments often move slower, and tracking systems must adapt to irregular schedules.
Geographical Barriers
Rivers, cliffs, and dense forests can delay shipments. Packages may need to be transferred between multiple carriers, each using different tracking technologies. This disrupts consistency in International Shipment Tracking data.
What Operational Challenges Do Companies Face?
Multiple Handovers
In remote deliveries, goods often pass through several carriers. Each handover risks data loss or inconsistent tracking updates. Customers may only see generic statuses like “in transit” for days.
High Costs
Reaching remote destinations requires more resources—special vehicles, local couriers, and manual labor. Tracking systems must integrate these non-standard methods, which increases costs.
Security Concerns

Remote regions may have higher risks of theft or package tampering. Without strong tracking, it becomes difficult to detect where and when a problem occurred.
Can Technology Solve These Tracking Problems?
GPS and IoT Devices
Smart GPS trackers and IoT sensors can provide location data even in areas with poor network coverage. Once connected to a signal, the device uploads stored data, filling the tracking gap.
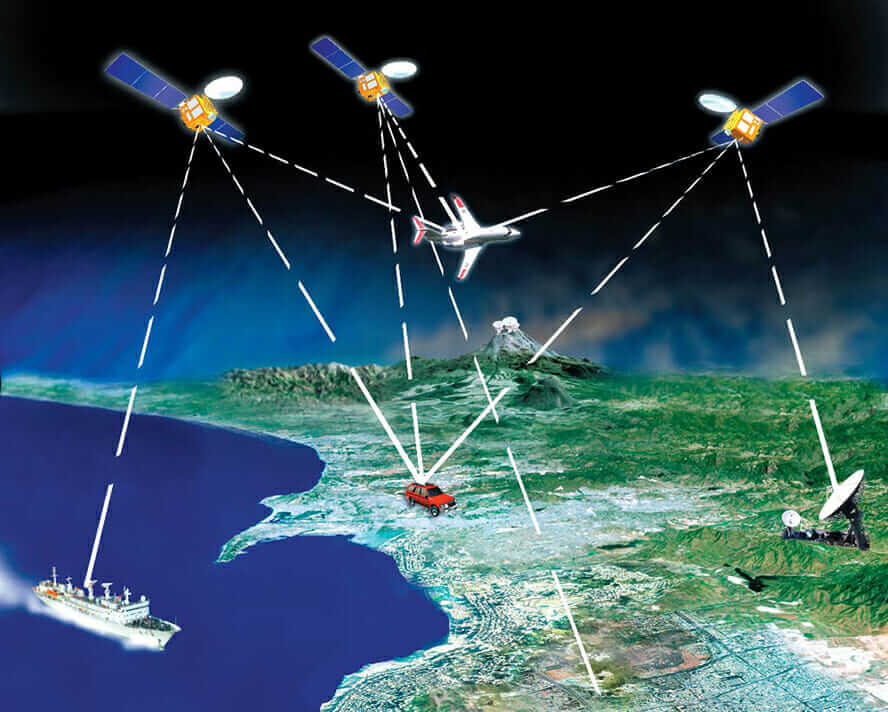
Satellite Communication
For areas without mobile networks, satellite-based tracking offers a reliable alternative. While costly, it ensures real-time International Shipment Tracking even in deserts, oceans, or high mountains.
Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
Drones are being tested to deliver small packages in hard-to-reach areas. Autonomous ground vehicles also help bridge the last-mile gap, and both can provide built-in tracking updates.
What Strategies Can Businesses Use?
- Hybrid Tracking Systems
Combine mobile, GPS, and satellite tracking for layered accuracy.
- Local Partnerships
Work with local couriers familiar with the terrain. They can provide manual updates that feed into global tracking systems. - Offline Data Storage
Equip devices to store tracking data offline and upload it once the signal is available. - Customer Communication
Manage expectations by informing buyers that tracking in remote areas may show longer gaps. Transparency reduces frustration. - Investment in Infrastructure
Collaborate with governments and NGOs to improve connectivity in remote regions. This benefits both logistics and local communities.
How Do These Challenges Affect Different Stakeholders?
For Online Sellers
Remote-region buyers may hesitate to purchase due to uncertain tracking. Sellers need strong International Shipment Tracking to build trust and encourage repeat business.
For Logistics Companies
They face higher operational costs and must adapt technology to challenging environments. Investing in advanced solutions is crucial to stay competitive.
For Buyers
Customers in remote areas may accept longer delivery times but still expect visibility. Without reliable tracking, confidence in international shopping declines.
Real-World Examples of Remote Tracking Challenges
Deliveries in the Himalayas
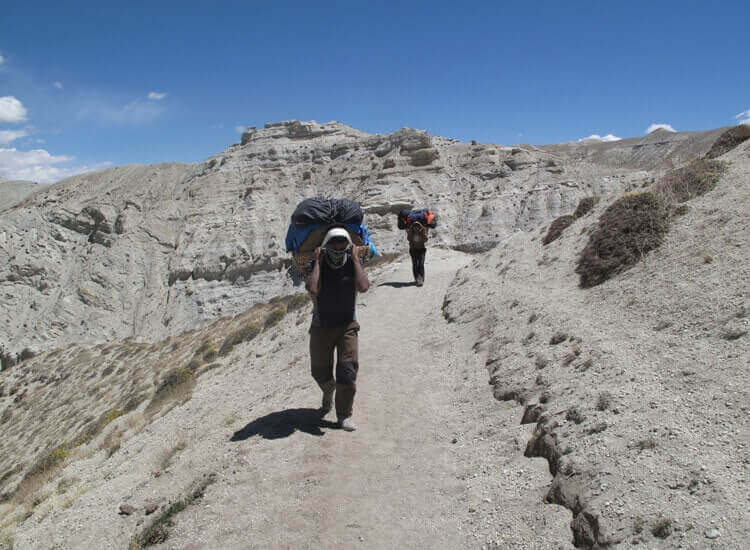

Mountain villages in Nepal rely on porters and small aircraft. Tracking updates often stop once shipments leave major cities, leaving customers unsure until delivery.
Amazon Rainforest Regions
Remote Amazonian towns depend on riverboats. Packages can take weeks, and tracking systems struggle to provide accurate updates until goods reach larger hubs.
African Rural Areas
In countries with poor road infrastructure, goods may switch between trucks, motorcycles, and even bicycles. Each mode creates tracking gaps that confuse customers.
Why Does Visibility Matter More in Remote Areas?
In remote deliveries, visibility is not just about convenience—it is about trust. Customers living far from urban centers already expect longer wait times. But when International Shipment Tracking shows nothing for days, frustration grows. Transparent updates, even if infrequent, assure customers their package is moving. Visibility becomes a competitive advantage for businesses that can maintain it.
What Are the Long-Term Solutions?
- Wider use of satellite tracking to cover underserved regions.
- Investment in renewable energy to power tracking devices off-grid.
- Development of global logistics standards to unify tracking across different carriers.
- Continuous innovation in autonomous delivery vehicles.

Key Lessons for Businesses
- Remote regions face unique challenges for International Shipment Tracking.
- Infrastructure, environment, and costs create major barriers.
- Technology like GPS, IoT, and satellites can reduce gaps but requires investment.
- Clear communication with customers is just as important as technical solutions.
- Long-term growth depends on building reliable, resilient tracking systems worldwide.
Conclusion
International Shipment Tracking in remote regions is far from simple. Businesses must balance cost, technology, and customer expectations to keep operations efficient. By embracing hybrid solutions, local partnerships, and transparency, companies can overcome the barriers of geography and infrastructure.
For logistics providers and online sellers, the future lies in building systems that work everywhere, not just in urban centers. Reliable tracking builds trust, even in the world’s hardest-to-reach locations.
To explore advanced solutions that simplify International Shipment Tracking, visit Postalparcel.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua