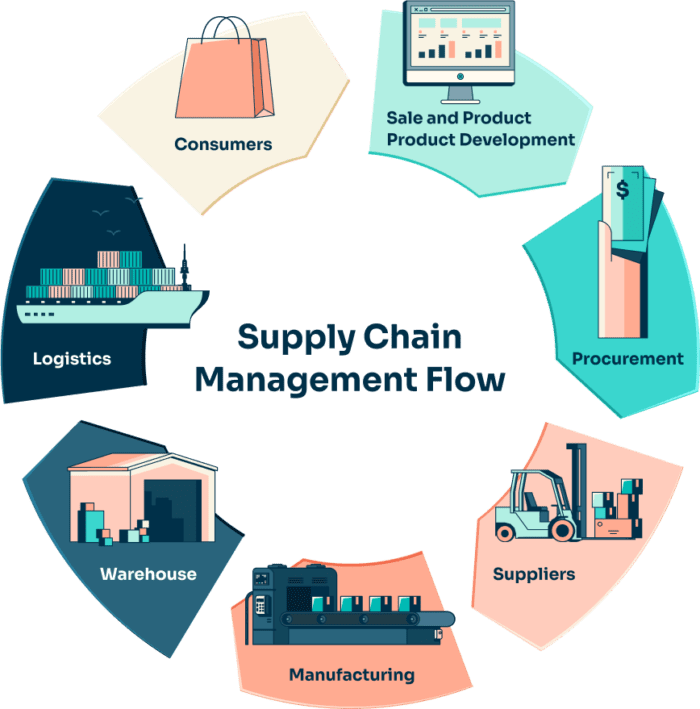
Reverse Logistics vs Forward Logistics: Key Differences and Synergies
In today’s competitive supply chain management landscape, understanding the difference between reverse logistics and forward logistics is crucial for businesses aiming to streamline their operations. While forward logistics focuses on the movement of goods from suppliers to customers, reverse logistics deals with the return flow of products. Although these two processes might seem separate, they are intrinsically linked and offer significant synergies that businesses can leverage. This article explores the key differences and synergies between reverse logistics and forward logistics, and how integrating them can improve operational efficiency.
What is Forward Logistics?
Forward logistics refers to the traditional flow of goods within the supply chain, from production to delivery to the final consumer. It includes all the processes that ensure products reach customers, including storage, transportation, and delivery. Forward logistics is primarily concerned with fulfilling customer orders, maintaining stock, and optimizing delivery routes to ensure timely arrivals.
Key Components of Forward Logistics:
- Inventory Management: Ensuring products are available in the right quantity and location.
- Order Fulfillment: Picking, packing, and shipping products to customers.
- Transportation and Delivery: Coordinating the delivery of goods from warehouses or manufacturers to customers.
Forward logistics is focused on maximizing efficiency in delivering products to customers while minimizing costs.
What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the process of managing product returns, recalls, and recycling. Unlike forward logistics, which focuses on moving goods from producers to customers, it handles the movement of goods in the opposite direction—back from customers to manufacturers or retailers. This process includes returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal of goods that are no longer needed or that are faulty.
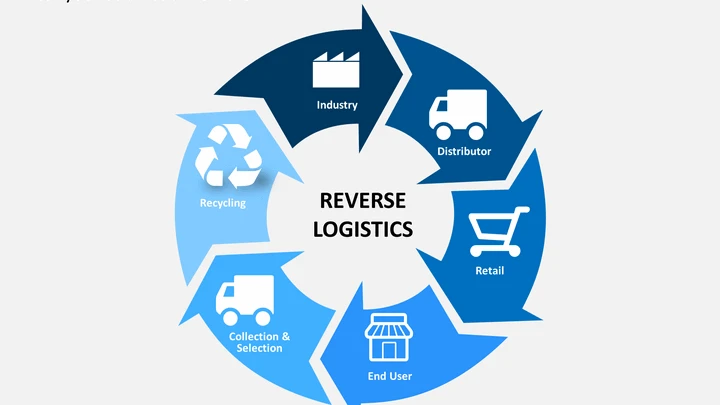
Key Components of Reverse Logistics:
- Returns Management: Handling product returns and exchanges.
- Repair and Refurbishment: Managing items that require repair or restoration.
- Recycling and Disposal: Processing unsellable or obsolete products for recycling or disposal.
Effective reverse logistics in supply chain management is essential for minimizing costs, managing waste, and improving sustainability efforts. Additionally, reverse logistics tracking is crucial for ensuring that returns are processed efficiently and that customers are satisfied with the resolution.
Key Differences Between Reverse Logistics and Forward Logistics
While both forward logistics and reverse logistics are essential to a successful supply chain, they serve different purposes and require distinct processes and strategies.
1. Direction of Goods Flow
- Forward Logistics: Goods move from the manufacturer or supplier to the consumer.
- Reverse Logistics: Goods move from the consumer back to the manufacturer or retailer for returns, repairs, or disposal.
2. Purpose
- Forward Logistics: The purpose is to fulfill customer demand, ensuring the timely delivery of goods.
- Reverse Logistics: The goal is to manage the return of goods, whether for repair, recycling, or disposal, and ensure customer satisfaction.
3. Processes Involved
- Forward Logistics: Involves inventory management, packaging, shipping, and distribution.
- Reverse Logistics: Includes managing returns, processing refunds, repairing damaged goods, and handling product recalls.
4. Cost Implications
- Forward Logistics: Generally involves lower costs since products are being delivered to customers.
- Reverse Logistics: Often incurs higher costs, as returns can lead to additional transportation, restocking, and disposal expenses.
While these two processes are quite different, they must be integrated for optimal supply chain management. A robust reverse logistics system can complement forward logistics by enhancing customer satisfaction, improving inventory management, and reducing waste.

Synergies Between Reverse Logistics and Forward Logistics
Although reverse logistics and forward logistics have distinct goals and processes, when integrated effectively, they create significant synergies that can improve efficiency and reduce costs for businesses. By aligning reverse logistics with forward logistics, businesses can streamline their operations, enhance customer service, and improve sustainability.
1. Improved Inventory Management
By tracking returns through reverse logistics tracking, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer preferences and product issues. This information can be used to adjust inventory and make better decisions in forward logistics, ensuring that popular products are always in stock and defective products are removed from circulation.
2. Cost Reduction
Integrating reverse logistics with forward logistics can lead to cost savings. By consolidating return shipments with outbound shipments, businesses can reduce transportation costs. Additionally, managing returns efficiently ensures that products are restocked and resold quickly, maximizing profitability.
3. Customer Satisfaction
A well-managed reverse logistics process helps businesses address customer issues promptly. By offering hassle-free returns and exchanges, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction. This, in turn, leads to better customer retention and loyalty.

4. Sustainability
Effective reverse logistics processes also contribute to sustainability efforts. By recycling or repurposing returned products, businesses can reduce waste and contribute to a circular economy. This not only benefits the environment but also improves a company’s reputation as a responsible business.
How Reverse Logistics Tracking Improves the Process
Reverse logistics tracking is essential for managing returns and exchanges efficiently. By providing real-time updates on the status of returns, businesses can ensure that products are processed and restocked quickly. Additionally, customers can track their returns, ensuring a smooth and transparent process.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics Tracking:
- Transparency for Customers: Customers can check the status of their returns, improving their experience and trust in the business.
- Faster Processing: Tracking helps businesses speed up the return process, reducing delays and ensuring products are quickly restocked or recycled.
- Better Data for Decision Making: By tracking returns, businesses can gather valuable data on product performance and customer behavior, helping to optimize both forward and reverse logistics.
Effective reverse logistics tracking ensures that businesses remain in control of their operations, reducing costs and improving overall efficiency.

Conclusion: The Key to a Successful Supply Chain
Understanding the differences and synergies between reverse logistics and forward logistics is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain. By integrating reverse logistics into the overall logistics strategy, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. With the help of advanced reverse logistics tracking, companies can ensure that returns and exchanges are processed quickly and efficiently, contributing to a smoother, more effective supply chain.
To streamline your reverse logistics process, explore solutions at PostalParcel. We offer innovative tools for managing reverse logistics and tracking returns, ensuring that your supply chain is optimized for success.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua