AI and Robotics in Warehouse Management Systems
In today’s highly dynamic supply chain environment, warehouse operations have evolved from simple storage spaces to complex, technology-driven hubs of activity. Among the most transformative technologies reshaping these operations are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics. These two forces are revolutionizing warehouse management systems (WMS), optimizing efficiency, accuracy, and scalability like never before.
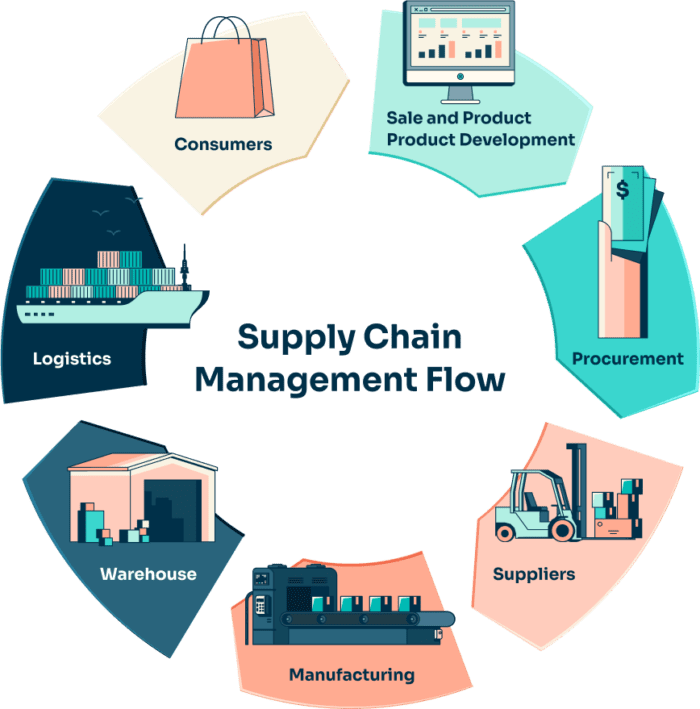
I. The Evolution of Warehouse Management
Traditional warehouse management systems primarily focused on inventory control, manual order picking, and basic tracking. However, the explosive growth of e-commerce, omnichannel fulfillment, and same-day delivery expectations have exposed the limitations of manual operations. Modern warehouses now demand intelligent, automated systems capable of managing increasing complexity and volume with precision and speed.
II. Role of Artificial Intelligence in Warehouse Management

Artificial Intelligence brings cognitive capabilities to WMS, enabling systems to make data-driven decisions, learn from patterns, and continuously improve.
1. Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
AI algorithms analyze historical sales, market trends, and seasonal patterns to predict product demand. This enables better inventory planning, reduces overstock or stockouts, and enhances customer satisfaction.
2. Optimized Inventory Allocation
AI can determine the best placement of products within the warehouse based on velocity, frequency of picking, and order history. This ensures faster access and minimizes picker travel time.
3. Automated Decision-Making
Through machine learning models, AI enables real-time decision-making—such as rerouting tasks during system delays or assigning labor based on workload forecasting. These decisions help maintain efficiency even during disruptions.
4. Intelligent Order Prioritization
AI helps prioritize orders based on shipping deadlines, customer importance, or delivery zones, ensuring high-value or urgent orders are processed first.
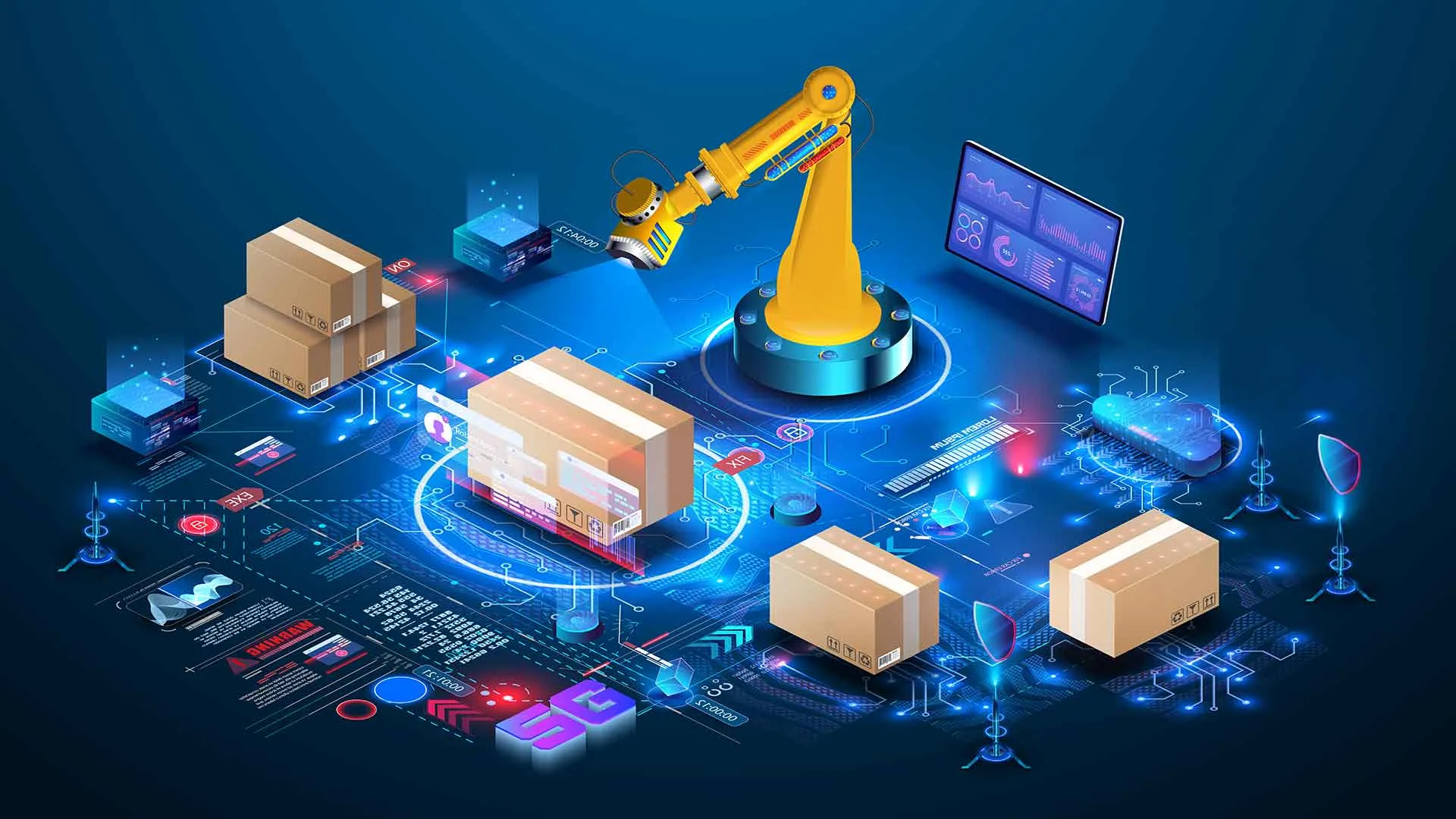
III. Robotics in the Warehouse: Changing the Physical Landscape
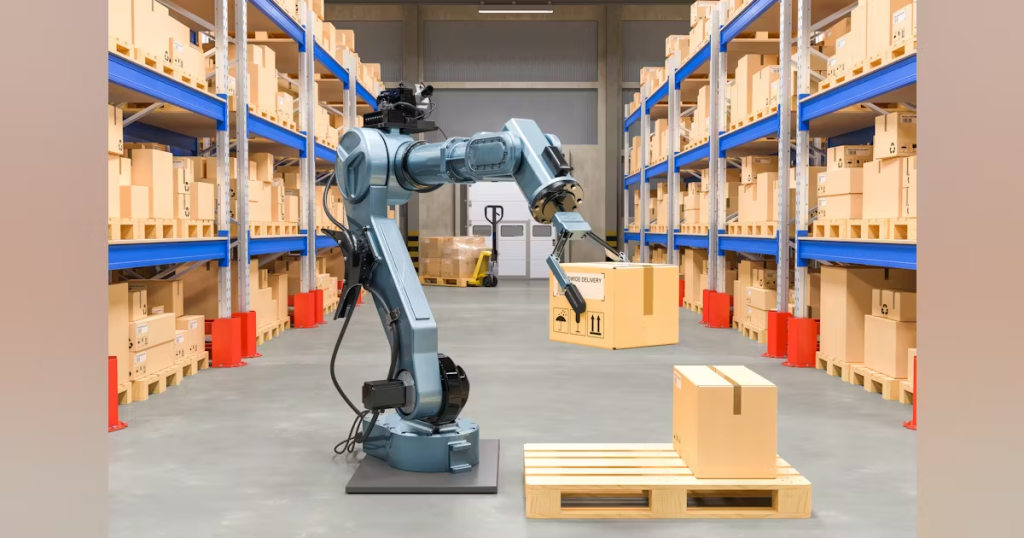

While AI handles the cognitive side of WMS, robotics executes the physical tasks, often replacing or augmenting human labor in repetitive and time-sensitive roles.
1. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Unlike traditional Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), AMRs navigate freely within the warehouse using sensors and AI. They transport goods between zones, assist in picking, and reduce congestion in high-traffic areas.
2. Robotic Picking Systems
Robotic arms integrated with machine vision and AI can identify, grasp, and sort various items with precision. These systems are particularly useful in high-volume environments where speed and accuracy are critical.
3. Sorting and Packing Robots
Automated sorting systems use AI to read barcodes and dynamically route packages to the correct chute. In packing stations, robots automate box selection, folding, sealing, and labeling.
4. Drones for Inventory Auditing
Some advanced warehouses now deploy drones equipped with cameras and scanners to conduct cycle counts and verify inventory, drastically reducing manual auditing time.
IV. Benefits of AI and Robotics Integration
Integrating AI and robotics into warehouse management systems offers a range of tangible benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated systems operate 24/7, reduce human error, and boost throughput.
- Lower Operational Costs: Despite high upfront investment, automation reduces long-term labor and inventory holding costs.
- Scalability: AI and robots can adapt to fluctuating demand without the need for extensive manual hiring or training.
- Data-Driven Insights: Real-time analytics allow managers to make informed decisions, optimize performance, and reduce waste.
V. Challenges and Considerations
Despite the advantages, implementation is not without challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Robotics and AI infrastructure can be costly for small to mid-sized businesses.
- Integration Complexity: Synchronizing new systems with legacy software may require customization and expert intervention.
- Workforce Displacement Concerns: While automation reduces manual labor, it also demands upskilling of existing workers to manage and maintain new systems.
VI. The Future Outlook

The future of warehouse management lies in fully integrated, intelligent ecosystems where AI and robotics operate in harmony. With advancements in 5G, IoT, and edge computing, the next generation of WMS will be even more responsive, autonomous, and capable of predictive decision-making. Human workers will shift from labor-intensive tasks to strategic roles—managing, analyzing, and improving warehouse systems.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence and robotics are no longer futuristic concepts—they are fundamental components of the modern warehouse. By transforming everything from inventory forecasting to order fulfillment, they enable businesses to meet rising customer expectations and operate with unprecedented agility. As competition intensifies across industries, those who embrace intelligent automation will lead the way in speed, precision, and innovation.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua