Der Schritt-für-Schritt-Leitfaden für den Rückverfolgungsprozess in der Logistik für ein effektives Retourenmanagement
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1. Why Reverse Logistics Tracking Process matters for returns management
- 2. Step-by-step Reverse Logistics Tracking Process
- 2.1 Step 1: Return request and authorization
- 2.2 Step 2: Return label and tracking ID
- 2.3 Step 3: First scan and carrier acceptance
- 2.4 Step 4: In-transit tracking updates
- 2.5 Step 5: Delivery to return facility
- 2.6 Step 6: Receiving and intake scan
- 2.7 Step 7: Inspection and decision
- 2.8 Step 8: Refund or exchange execution
- 2.9 Step 9: Inventory update and closure
- 3. Handling exceptions in the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process
- 4. How postalparcel supports return tracking
- 5. Customer questions you should answer clearly
- Schlussfolgerung
Verfolgung der umgekehrten Logistik Process plays a critical role in modern returns management. Customers expect clear updates, while sellers need visibility, control, and cost reduction. A structured Reverse Logistics Tracking Process helps both sides stay aligned from the moment a return is requested to the final refund or exchange.
This guide explains each step in a clear, practical way, with a focus on execution rather than theory.
1. Why Reverse Logistics Tracking Process matters for returns management
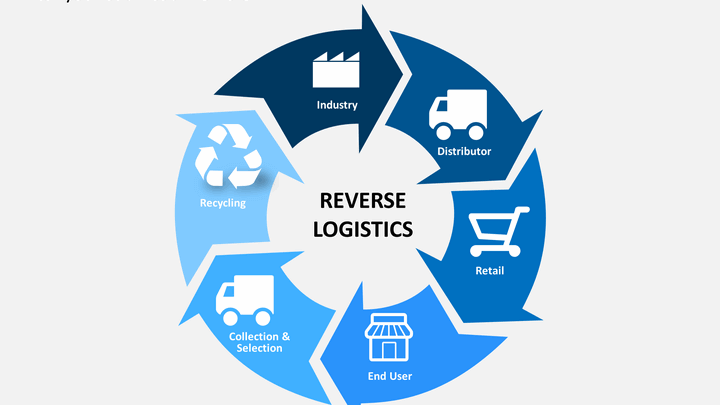
Returns affect customer trust, Inventar accuracy, and cash flow. Without a clear Reverse Logistics Tracking Process, packages get delayed, refunds slow down, and support tickets increase.
A well-designed process helps you:
- Track every return in real time
- Reduce “Where is my refund?” inquiries
- Detect return fraud earlier
- Speed up restocking and resolution
1.1 What reverse logistics tracking really means
Reverse logistics tracking follows returned items as they move backward through the supply chain. A solid Reverse Logistics Tracking Process answers simple questions at every stage:
- Where is the return now?
- What step comes next?
- Who is responsible at this stage?
- When will the customer see an update?
2. Step-by-step Reverse Logistics Tracking Process
Each step below should create a visible status update. Clear checkpoints prevent confusion and reduce manual follow-ups.
2.1 Step 1: Return request and authorization
The Reverse Logistics Tracking Process starts when a customer requests a return. This step should confirm order details and set expectations early.
Key actions:
- Verify order number and customer identity
- Capture return reason with fixed options
- Confirm return window and item condition
Tracking statuses:
- Return requested
- Return approved
- RMA issued
2.2 Step 2: Return label and tracking ID

Every return must have a unique tracking ID. This ID connects the package to the order and the return case.
Bewährte Praktiken:
- One tracking ID per package
- Barcode or QR code linked to the RMA
- Correct return address based on item type
This step forms the backbone of the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process.
2.3 Step 3: First scan and carrier acceptance
Many disputes happen before the first scan. A label alone does not confirm movement.
Important tracking events:
- Etikett erstellt
- Dropped off or picked up
- Accepted by carrier
Once the carrier scans the package, the Verfolgung der umgekehrten Logistik Process officially begins.
2.4 Step 4: In-transit tracking updates
Returns often move slower than outbound shipments. Still, regular updates matter.
Recommended milestones:
- Im Transit
- Arrived at sorting hub
- Departed sorting hub
If scans stop for several days, trigger an alert. A strong Reverse Logistics Tracking Process reacts before customers complain.

2.5 Step 5: Delivery to return facility
This is a critical moment for customers. Many expect refunds soon after delivery.
Tracking event:
- Delivered to return center
Action to take:
- Notify the customer immediately
- Start the internal inspection timer
2.6 Step 6: Receiving and intake scan
Delivery does not mean the item entered the Lagerhaus system. Intake confirms physical receipt.
Internal tracking events:
- Received at dock
- Sorted for inspection
This step prevents gaps between carrier data and warehouse reality in the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process.
2.7 Step 7: Inspection and decision
Inspection determines the final outcome of the return.
Possible statuses:
- Under inspection
- Approved for refund
- Approved for exchange
- Return rejected
Inspection checks usually include:
- Correct item and SKU
- Condition match
- Accessories included
- Signs of use or damage

2.8 Step 8: Refund or exchange execution
This stage links Logistik with payments. A complete Reverse Logistics Tracking Process shows financial progress clearly.
Tracking events:
- Refund initiated
- Erstattung abgeschlossen
- Exchange shipped
If an exchange ships, link the new outbound tracking to the same return case.
2.9 Step 9: Inventory update and closure
The final step closes the loop.
Inventory actions:
- Restocked as sellable
- Moved to clearance
- Sent for repair or disposal
Fast inventory updates improve availability and reporting accuracy.
3. Handling exceptions in the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process
No process works perfectly every time. Exception handling defines overall quality.

3.1 Common return issues
- No scan after label creation
- Package stuck in transit
- Delivered but not received internally
- Wrong or missing item
- Empty box claims
3.2 Simple escalation rules
Set clear response timers:
- No first scan in 72 hours → notify customer
- No movement in 5–7 days → carrier trace
- Delivered but not received in 48 hours → warehouse check
This keeps the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process predictable and controlled.
4. How postalparcel supports return tracking
Postpaket helps centralize all return events into one timeline. Instead of switching between carriers and systems, teams see one continuous view.
Key elements to track together:
- Carrier scan data
- RMA and order reference
- Warehouse intake and inspection
- Refund or exchange status
- Ausnahmewarnungen
4.1 Clear status mapping for customers
Carrier messages can be confusing. Mapping them into simple statuses improves trust and understanding within the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process.
Beispiel:
- “Shipment information received” → Label created
- “Arrived at facility” → At sorting hub
- “Delivered” → Return received
5. Customer questions you should answer clearly

5.1 Why is my return not moving yet?
Tracking starts only after the carrier scans the package. Label creation alone does not start the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process.
5.2 Why hasn’t my refund started after delivery?
Refunds usually begin after intake and inspection. Lieferung is only one step in the Reverse Logistics Tracking Process.
5.3 What happens if my return is delayed?
The seller can open a carrier investigation and update the return case. Clear tracking reduces uncertainty.
5.4 Can I track exchanges the same way?
Yes. A strong Reverse Logistics Tracking Process links the return and the replacement shipment in one case.
5.5 What if the wrong item is returned?
Inspection results, photos, and weight checks help resolve the case and decide next steps.
Schlussfolgerung
A clear Reverse Logistics Tracking Process turns returns from a problem into a controlled workflow. When each step has a visible status, clear ownership, and simple rules, customers stay informed and teams stay efficient. With centralized tracking and structured milestones, platforms like postalparcel help you manage returns with confidence and consistency.
Einblicke in die Industrie
Nachrichten über den Posteingang
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua