Was ist ein Lagerverwaltungssystem? Ein anfängerfreundlicher Leitfaden
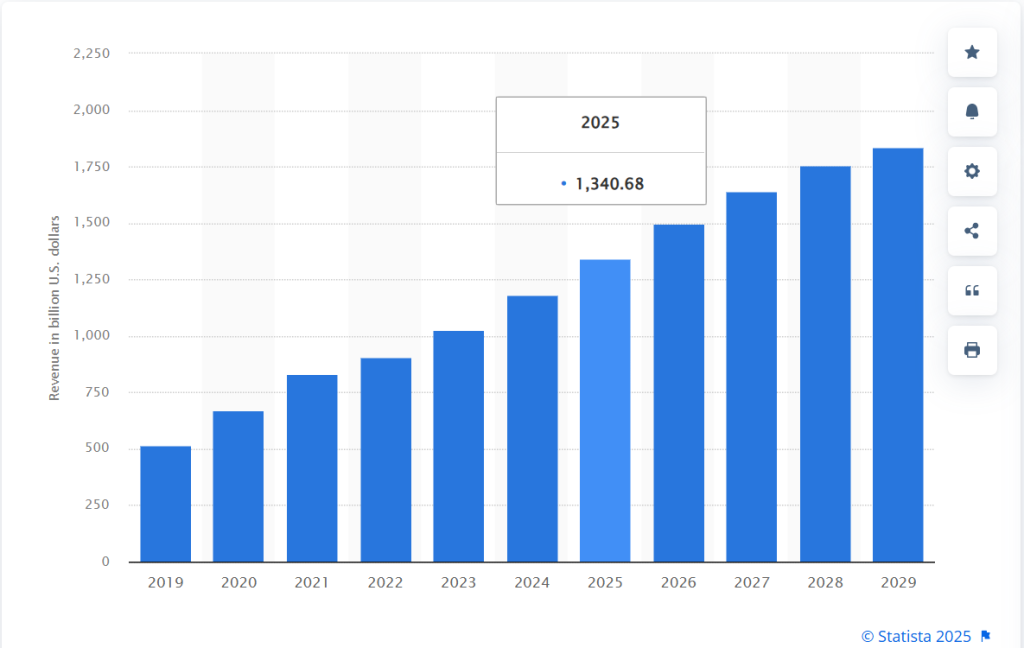
In einer Zeit, in der die digitale Transformation jeden Winkel des Handels umgestaltet, ist ein effizienter Lagerbetrieb wichtiger denn je. Laut Statistawurde prognostiziert, dass der Umsatz der US-E-Commerce-Branche bis 2029 $1,8 Billionen erreichen wird, was einem Wachstum von 37,16% zwischen 2025 und 2029 allein. Da die Auftragsvolumina in die Höhe schnellen und die Erwartungen der Verbraucher steigen, sehen sich die Unternehmen einem wachsenden Druck ausgesetzt, die Auftragsabwicklung zu rationalisieren, Fehler zu minimieren und die Lieferzeiten zu verkürzen. Dies wirft eine entscheidende Frage auf:
Wie können Unternehmen immer komplexere Lagerabläufe präzise und skalierbar verwalten?
Die Antwort liegt in der Umsetzung eines Lagerverwaltungssystem (WMS)ein leistungsstarkes Software-Tool, das die Genauigkeit, Automatisierung und Transparenz im gesamten Lager und darüber hinaus fördert. A WMS vereinfacht den Lagerbetrieb und ermöglicht die nahtlose Integration mit anderen Supply-Chain-Management-Tools, so dass Unternehmen Einblicke in Echtzeit erhalten und sich schnell an veränderte Anforderungen anpassen können.
Was ist ein Lagerverwaltungssystem (WMS)?
Ein Warehouse Management System (WMS) ist eine Softwarelösung, die Unternehmen bei der Steuerung und Optimierung von Lagerabläufen unterstützt, z. B. Bestandsverwaltung, Auftragsabwicklung und Personalverwaltung. Ein WMS bietet durchgängige Transparenz und Kontrolle über den gesamten Lagerprozess und ersetzt veraltete manuelle Hilfsmittel wie Tabellenkalkulationen oder Klemmbretter durch ein zentrales, automatisiertes System. Dies führt zu höherer Effizienz, Genauigkeit und besserer Entscheidungsfindung.
Ein WMS verbessert die betriebliche Leistung und hilft Unternehmen, die Anforderungen ihrer Kunden schneller und effizienter zu erfüllen, indem es den Bestand in Echtzeit verfolgt, die Arbeitsressourcen verwaltet und die Arbeitsabläufe rationalisiert.
Wichtige Funktionsbereiche eines Lagerverwaltungssystems (WMS)
1. Entgegennahme und Einlagerung
Ein Warehouse Management System (WMS) rationalisiert den Wareneingangsprozess, indem es den Wareneingang, die Validierung und die Standortzuweisung automatisiert. Moderne WMS-Systeme integrieren RFID-Technologie, Barcode-Scanner und digitale Bestellsysteme, um den Prozess zu automatisieren:
- Überprüfung der Artikel anhand von Rechnungen oder Bestellungen
- Etikettengenerierung für schnellere Identifizierung
- Intelligente Standortzuweisung auf der Grundlage von Bestandsrotation oder temperatursensiblen Lageranforderungen
Dies verbessert die Genauigkeit und Geschwindigkeit, schafft eine solide Grundlage für den Rest der Lieferkette und minimiert manuelle Fehler.
2. Bestandsverwaltung in Echtzeit
Ein wesentliches Merkmal eines Lagerverwaltungssystems (LVS) ist die Fähigkeit, Echtzeittransparenz über die Lagerbestände im gesamten Lager und in der Lieferkette zu schaffen. Durch den Einsatz von Technologien zur automatischen Identifizierung und Datenerfassung (AIDC) wie Barcodes und RFID können Unternehmen:
- Artikelstandort und -menge jederzeit verfolgen
- Sie erhalten Warnungen über niedrige Lagerbestände und automatische Auslöser für den Nachschub
- Zuteilung von Beständen auf der Grundlage einer benutzerdefinierten Logik (z. B. FIFO, LIFO)
- Integration von Zykluszählung und Bedarfsprognose
Diese Echtzeitverfolgung ermöglicht es Unternehmen, ihre Bestände zu verschlanken, Fehlbestände zu vermeiden und die Genauigkeit der Auftragsabwicklung zu verbessern, was die Kundenzufriedenheit insgesamt erhöht.
3. Kommissionierung, Verpackung und Erfüllung von Aufträgen
Die Kommissionierung ist einer der ressourcenintensivsten Prozesse in einem Lager und macht bis zu 55% der gesamten Lagerkosten aus (ResearchGate). Ein WMS reduziert diese Kosten durch Optimierung:
- Auswahl der Pfade
- Batch-, Zonen- oder Cluster-Picking-Techniken
- Technologien wie Pick-to-Light, Pick-to-Voice und RF-Verifizierung
- Fortgeschrittene Algorithmen und Robotik zur Pfadoptimierung

Durch die Verbesserung der Kommissioniereffizienz ermöglicht ein WMS ein schnelleres und genaueres Verpacken und Versenden von Aufträgen, was in hochvolumigen E-Commerce-Umgebungen entscheidend ist.
4. Integration von Versand und Transportunternehmen
Versandprozesse können oft zu Engpässen im Lagerbetrieb werden. Ein modernes Lagerverwaltungssystem (WMS) lässt sich nahtlos mit Transportverwaltungssystemen (TMS) und Spediteuren integrieren und automatisieren:
- Erstellung von Packlisten und Rechnungen
- Erstellung von Konnossementen (BOL)
- Druck von Trägeretiketten
- Versandbenachrichtigungen und Sendungsverfolgung in Echtzeit
Diese Integrationen gewährleisten pünktliche Lieferungen und eine bessere Sichtbarkeit der letzten Meile, was die Kundenzufriedenheit erhöht und betriebliche Verzögerungen reduziert.
5. Arbeitsverwaltung
Die Arbeitsverwaltung ist eine weitere wichtige Funktion eines Lagerverwaltungssystems (LVS). Indem es Einblicke in die Produktivität der Mitarbeiter bietet, kann ein WMS hilft Unternehmen:
- Verfolgen Sie die Effizienz der Mitarbeiter und die Dauer der Aufgabenerledigung
- Optimierung der Arbeitskostenverteilung
- Ermittlung von Produktivitätslücken und Qualifikationsdefiziten
- Verkürzung der Reisezeit durch Verschachtelung von Aufgaben
So können Unternehmen ihre Mitarbeiter effizienter und flexibler einsetzen, Leerlaufzeiten reduzieren und die Gesamtproduktivität steigern.
6. Werft- und Dockmanagement
Die Verwaltung von Hof- und Dockvorgängen ist für Lager mit hohem LKW-Aufkommen von entscheidender Bedeutung. Ein WMS mit Hof- und Dockmanagementfunktionen hilft dabei:
- Lkw zur richtigen Laderampe leiten
- Unterstützung von Cross-Docking, bei dem Waren ohne Zwischenlagerung direkt in ausgehende Sendungen übernommen werden
- Automatischer Abgleich von Belegen mit aktiven Kundenaufträgen in Echtzeit
Diese Funktionalität ist vor allem für Branchen wie die Kühlkettenlogistik von Vorteil, in denen zeitempfindliche Produkte schnell bearbeitet werden müssen, um die Qualität zu erhalten.
7. Analytik und Leistungsmetriken
Ein Lagerverwaltungssystem (LVS) sammelt und analysiert kontinuierlich Echtzeit-Betriebsdaten. Diese Daten werden verwendet, um wichtige Leistungsindikatoren (KPIs) zu verfolgen, wie z. B.:
- Pünktliche Versandtarife
- Genauigkeit der Bestandsaufnahme
- Auftragsdurchlaufzeit und Kommissioniergenauigkeit
- Füllungsraten und Vertriebskosten
Unternehmen können diese Erkenntnisse nutzen, um die Leistung zu überwachen, Arbeitsabläufe zu optimieren und datengestützte Entscheidungen zu treffen, die zu einer kontinuierlichen Verbesserung des Lagerbetriebs führen.

Warum jedes wachsende Unternehmen ein WMS braucht
Ein Lagerverwaltungssystem (LVS) ist für Unternehmen, die ihren Betrieb effizient skalieren und Kosten senken wollen, unerlässlich. Einige häufige Herausforderungen, die ein WMS lösen kann, sind:
- ungenaue Bestandsaufzeichnungen
- Hohe Auftragsfehlerquoten und Rückläufer
- Lagerüberlastung und Ineffizienzen
- Steigende Arbeitskosten ohne entsprechende Produktivitätssteigerungen
- Mangelnde Transparenz im Lagerbetrieb
Durch die Einführung eines WMS können Unternehmen Folgendes erreichen:
- Geschwindigkeit und Effizienz: Schnellere Bearbeitung von ein- und ausgehenden Sendungen
- Kosteneinsparungen: Geringere Arbeits- und Betriebskosten
- Genauigkeit: Bessere Auftragsgenauigkeit und weniger Retouren
- Skalierbarkeit: Nahtlose Erweiterung zur Handhabung höherer SKU-Zahlen oder mehrerer Standorte
- Sichtbarkeit: Eine einheitliche Echtzeit-Datenquelle für Lager-, Versand- und ERP-Systeme (Enterprise Resource Planning)
Wie man das richtige Lagerverwaltungssystem auswählt
1. Verstehen Sie Ihre Bedürfnisse
- Größe und Anordnung des Lagers
- Branchenspezifische Anforderungen (z. B. Kühllagerung, hoher SKU-Umschlag)
- Integrationsbedarf (ERP, CRM, TMS)
- Budget und erwarteter ROI-Zeitplan
2. Kernkompetenzen evaluieren
- Cloud-basierte oder Vor-Ort-Bereitstellungsoptionen?
- Unterstützung für mobile Geräte wie Handheld-Scanner und -Geräte?
- Erweiterte Kommissionier- und Automatisierungsfunktionen?
- Analyse- und Berichtsfunktionen?
3. Umsetzung Prozess
- Beginnen Sie mit einer Piloteinführung, um die Wirksamkeit des Systems zu testen.
- Gründliche Schulung aller Lagerfunktionen für eine reibungslose Einführung
- Überwachung der KPIs nach der Einführung und Vornahme der erforderlichen Anpassungen zur Optimierung der Leistung
Beispiel für einen realen Anwendungsfall
Szenario: Ein nationaler Online-Händler, der in der Weihnachtssaison im 4. Quartal ein dreifaches Volumenwachstum verzeichnet
Herausforderung: Fehler bei der manuellen Kommissionierung, verspätete Sendungen und Unstimmigkeiten im Bestand
Lösung: Implementierung eines cloudbasierten WMS, das mit Barcode-Scannern und Shopify integriert ist
Ergebnisse:
- 42% Verkürzung der Kommissionierzeit
- 99,7% Bestandsgenauigkeit
- 25% Steigerung des Auftragsvolumens ohne zusätzliches Personal
Durch die Einführung eines Lagerverwaltungssystems (LVS) können Unternehmen ihre Lagerabläufe erheblich optimieren und Genauigkeit, Geschwindigkeit und Skalierbarkeit gewährleisten. Mit dem richtigen WMS können Lagerhäuser betriebliche Herausforderungen meistern, Kosten senken und die Gesamtleistung verbessern - und damit die Kundenzufriedenheit steigern und das Unternehmenswachstum unterstützen.
Einblicke in die Industrie
Nachrichten über den Posteingang
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua




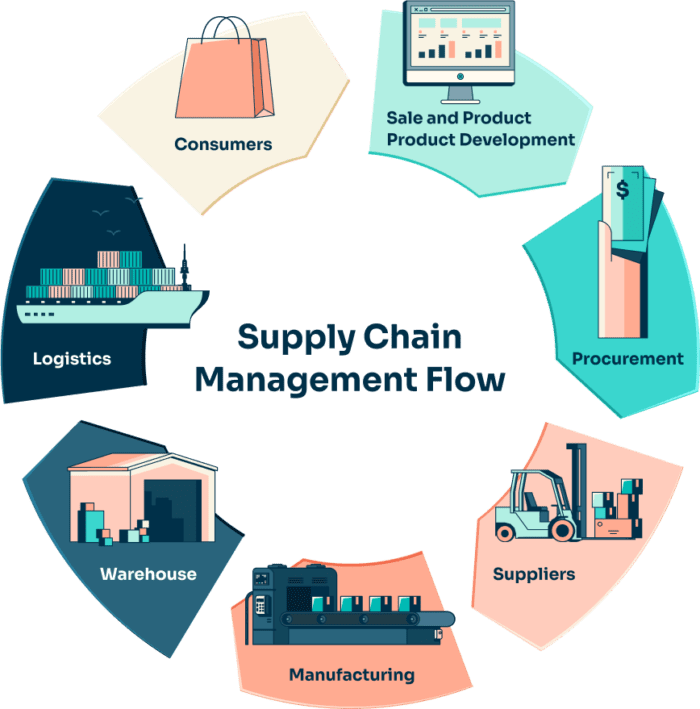



[...] die finanzielle und operative Gesundheit Ihres Unternehmens. Unabhängig davon, ob Sie sich für ein erstklassiges Lagerverwaltungssystem (LVS) oder ein bestehendes Modul in Ihrem ERP-System entscheiden, [...]
[...] Druck für eine taggleiche Lieferung, brauchen Unternehmen mehr als Tabellenkalkulationen und veraltete Tools. Ein modernes Warehouse Management System (WMS) bringt Struktur und Effizienz, indem es Arbeitsabläufe digitalisiert, Fehler reduziert und [...]
[...] Durch die Integration mit Warehouse-Management-Systemen (WMS) und ERP-Plattformen bietet ein TMS eine durchgängige Lieferkette [...]