What Is E-commerce Warehouse Logistics? A Beginner’s Guide
E-commerce has revolutionized how people shop, and behind every online order is a complex logistical system that ensures products arrive accurately and on time. This system’s core lies in e-commerce warehouse logistics, which keeps digital businesses running smoothly.
Whether you’re a new online seller or just curious about how WooCommerce and Shopify stores manage fast deliveries, this beginner’s guide will walk you through what e-commerce warehouse logistics is, how it works, and why it matters.

What Is E-commerce Warehouse Logistics?
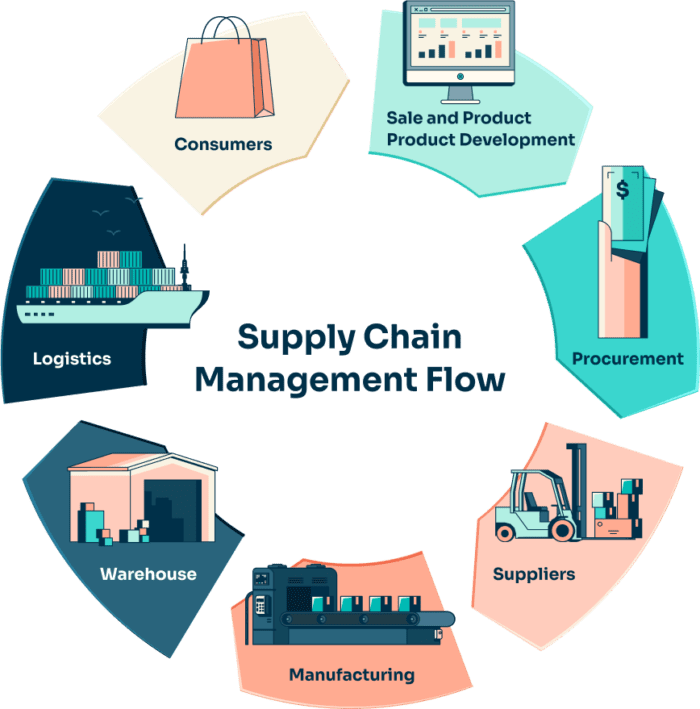
E-commerce warehouse logistics refers to storing, organizing, managing, and moving products within a warehouse or fulfillment center to fulfill online orders efficiently. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including:
- Inventory management
- Order picking and packing
- Shipping coordination
- Returns processing (reverse logistics)
- Warehouse space optimization
The ultimate goal is to ensure that the right product reaches the right customer at the right time with minimal cost and maximum accuracy.
Why Order Fulfillment Efficiency Is Crucial in E-commerce?

Unlike traditional retail, e-commerce businesses often deal with thousands of individual customers rather than bulk shipments to stores. It means:
- High order volume with diverse destinations
- Tight delivery timelines, especially with rising expectations for same-day or 2-day shipping
- Frequent returns, especially in industries like fashion
An optimized warehouse logistics system ensures faster fulfillment, fewer shipping errors, better customer experience, and a more profitable e-commerce business.
Key Components of E-commerce Warehouse Logistics
1. Inventory Management
At the heart of any warehouse operation is inventory control. You need to know:
- How much stock do you have
- Where is it located in the warehouse
- When to reorder
Many e-commerce businesses rely on PostalParcel’s services to effectively manage their inventory levels and ensure timely deliveries. With PostalParcel, businesses can easily track stock levels in real time, preventing overselling or stockouts. By using warehouse management systems (WMS), PostalParcel streamlines order fulfillment and optimizes the logistics process for both local and international shipping.
2. Warehouse Layout and Storage

An efficient warehouse layout reduces travel time for workers and speeds up order processing. Standard storage methods include:
- Racking systems (for bulk items)
- Bin shelving (for small SKUs)
- Zoning by product type or order frequency
Advanced warehouses use automation tools like robotic picking systems or conveyor belts to boost speed and accuracy.
3. Order Picking and Packing
This stage involves locating the products, verifying quantities, and preparing them for shipment.
Picking methods include:
- Single order picking – for low-volume orders
- Batch picking – for efficiency when multiple orders contain the same item
- Zone picking – different pickers work in specific zones, combining items at the packing stations
Packing must be done carefully to avoid damage, reduce dimensional weight, and maintain brand experience.
4. Shipping and Carrier Coordination
Once packed, orders are handed over to courier partners like UPS, FedEx, DHL, or local carriers. Warehouse systems often integrate directly with carrier platforms to generate labels and track deliveries.
Choosing the right shipping strategy—flat rate, real-time, or free shipping—also impacts logistics costs and customer satisfaction.
5. Returns and Reverse Logistics
Returns are inevitable in e-commerce. A good warehouse logistics setup includes:
- Designated return receiving areas
- Inspection and restocking processes
- Clear status updates for customer service teams
Efficient reverse logistics can save costs, reduce waste, and improve customer loyalty.
In-house Fulfillment vs. 4PL (Fourth-Party Logistics)
When managing warehouse logistics, e-commerce businesses have two options:
- In-house fulfillment: You own or rent a warehouse and manage everything internally
- Fourth-party logistics (4PL): You outsource logistics to fulfillment providers like ShipBob, Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), or DHL eCommerce
While in-house gives more control, 4PLs offer scalability, existing infrastructure, and access to distributed fulfillment centers.
Challenges in E-commerce Warehouse Logistics

Even with the best systems, e-commerce warehouse logistics faces several challenges:
- Inventory inaccuracies due to human error
- Seasonal demand spikes like Black Friday or Christmas
- Returns management complexity
- Labor shortages in peak seasons
- International shipping and customs delays
Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning, technology investment, and process improvement.
Final Thoughts
E-commerce warehouse logistics is the backbone of successful online selling. It may not be as visible as your website design or marketing campaigns, but it plays a crucial role in ensuring your customers receive what they ordered—quickly and accurately.
For beginners, start with:
- Understanding your inventory and customer demand
- Choosing the right tools (WMS or IMS)
- Designing a warehouse layout that fits your order volume
- Considering when to outsource to a 4PL
As your business grows, fine-tuning your warehouse logistics will become a support function and a competitive advantage.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua