IoT Breakthroughs Transform Logistics and Supply Chain
In today’s rapidly evolving digital economy, the Internet of Things (IoT) is driving a major transformation across industries, and logistics and supply chain management are at the forefront of this change. With its ability to connect physical assets—vehicles, containers, warehouses, and even products—to digital systems through smart sensors and networks, IoT enables companies to gain real-time visibility, control, and optimization like never before.
What is IoT in Logistics?
IoT in logistics refers to the use of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data throughout the supply chain. These devices include:
- RFID tags for tracking items,
- GPS trackers for fleet monitoring,
- Temperature and humidity sensors for environmental control,
- Smart cameras and AI-enabled scanners for warehouse operations.
By integrating IoT, companies can automate routine processes, reduce human error, and make proactive decisions using data analytics.
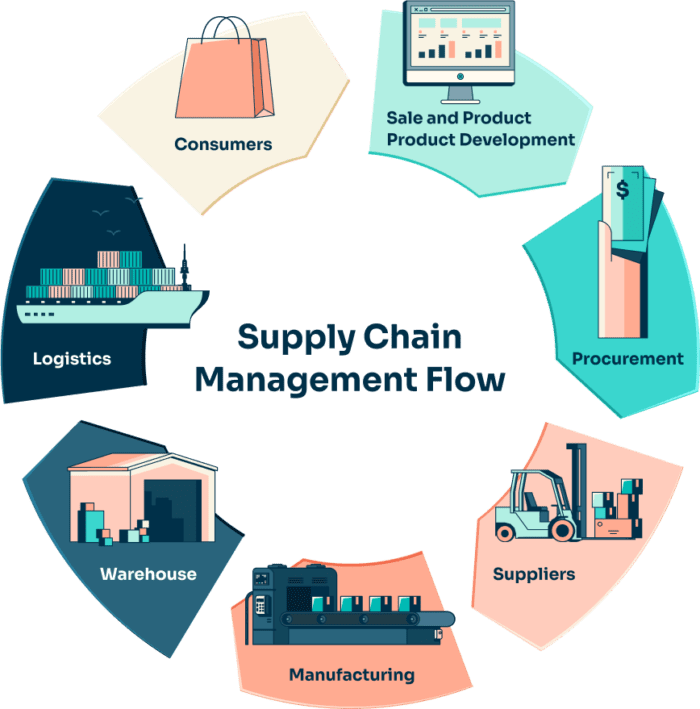
Core Applications of IoT in Supply Chain Management
1. Real-Time Tracking and Shipment Monitoring
With GPS-enabled devices and IoT sensors installed on vehicles and cargo, companies can monitor location, speed, and route deviations in real time. This not only helps in improving Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) accuracy but also ensures higher transparency for customers awaiting deliveries.
For example, logistics managers can detect if a shipment is stuck in traffic or delayed at a customs checkpoint, and immediately adjust downstream operations or inform the client.
2. Intelligent Inventory and Warehouse Automation
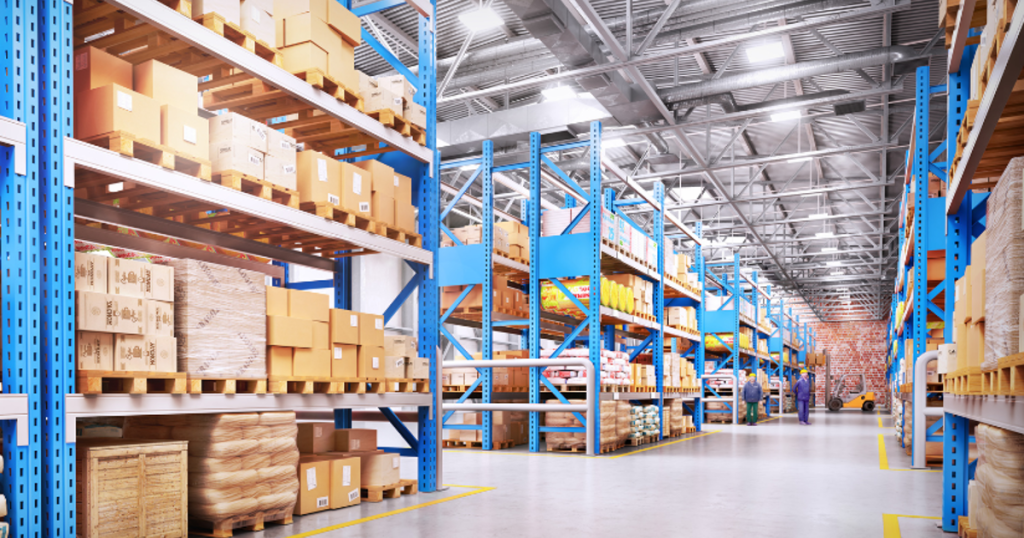

Modern warehouses equipped with IoT sensors and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can manage inventory dynamically. Smart shelves update stock levels in real time, and systems can automatically reorder products when inventory falls below a threshold.
This leads to:
- Reduced manual labor
- Fewer stockouts or overstocking
- Optimized space and faster picking processes
3. Condition Monitoring for Sensitive Goods
IoT plays a critical role in cold chain logistics, where the condition of goods is as important as their location. Sensors continuously measure temperature, humidity, light exposure, and vibrations during transit. If any parameter falls out of range, alerts are sent immediately, allowing for corrective measures such as rerouting or adjusting storage conditions.
This is vital for pharmaceuticals, fresh produce, and chemicals where quality compliance is non-negotiable.
4. Predictive Maintenance for Fleet Management
Vehicles and machinery equipped with IoT can report engine performance, tire pressure, fuel consumption, and other vital metrics. With this data, logistics providers can predict mechanical failures before they happen, schedule maintenance efficiently, and reduce unplanned downtime.
This enhances operational safety and lowers overall fleet maintenance costs.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making and Optimization
IoT-generated data provides supply chain managers with detailed insights into delivery performance, warehouse throughput, and demand trends. Combined with AI and machine learning, it allows for better forecasting, route planning, load optimization, and risk management.
This leads to:
- Lower logistics costs
- Faster delivery times
- Improved customer satisfaction
Key Benefits at a Glance

| IoT Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time tracking | Increased visibility and accountability |
| Smart inventory | Reduced manual errors and improved accuracy |
| Environmental monitoring | Protection of sensitive goods and compliance |
| Predictive analytics | Reduced downtime and cost-efficiency |
| Data integration | Agile, responsive, and data-driven supply chains |
Implementation Challenges
Despite its advantages, IoT adoption in logistics faces several challenges:
- High initial cost: Sensor networks, devices, and infrastructure investment.
- Data privacy and cybersecurity risks: More connected devices mean more vulnerabilities.
- Integration complexity: Legacy systems may be difficult to integrate with modern IoT platforms.
- Skilled workforce requirement: Operating and maintaining IoT ecosystems require trained personnel.
Future Trends: Beyond Visibility
IoT’s role will continue to expand as it converges with other emerging technologies such as:
- 5G for faster data transmission
- Blockchain for secure and tamper-proof tracking records
- Digital twins for virtual modeling of supply chain operations
These advancements will unlock next-level efficiency, automation, and sustainability for logistics ecosystems globally.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is fundamentally transforming how logistics and supply chains operate. It turns traditional, reactive systems into intelligent, interconnected networks that anticipate problems, respond quickly, and create competitive advantages. As companies navigate an increasingly complex global trade environment, those who embrace IoT will be best positioned to deliver speed, efficiency, transparency, and customer-centric service in the supply chain of tomorrow.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua