Managing Multi-Warehouse Operations with WMS: Real-Time Inventory Control
Introduction: The Complexity Behind Multi-Warehouse Inventory
Managing inventory across multiple warehouses is no small feat. Whether it’s two facilities in the same city or ten across different countries, the goal remains: maintain inventory accuracy, streamline fulfillment, and reduce operating costs.
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) plays a pivotal role in this process. It enables centralized control over key logistics functions, including receiving, storage, picking, packing, shipping, and accounting. When properly implemented, a WMS transforms warehouse chaos into operational clarity.

According to recent market research, the global warehouse automation market was valued at over $23 billion USD in 2023. With a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 15%, it is expected to reach $41 billion USD by 2027. This growth reflects the accelerating shift from manual to automated warehouse operations. Businesses increasingly turn to WMS as part of broader automation strategies to improve speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Challenges of Managing Multi-Warehouse Inventory
1. Real-Time Tracking Difficulties
Many businesses struggle with real-time inventory tracking due to disconnected systems or manual updates. This lack of centralization leads to:
- Inaccurate inventory counts
- Unavailable or outdated data
- Poor synchronization between warehouse and storefront
Without a single source of truth, decision-makers face blind spots in stock levels, location-specific availability, and reorder timing.
2. Inventory Imbalance
It’s common to see overstock in one location and understock in another. This imbalance drives up costs due to:
- Emergency transfers
- Rush shipping between facilities
- Lost sales from stockouts
Misallocation often stems from reactive inventory strategies and a lack of historical insights.
3. Order Fulfillment Delays
Order routing becomes inefficient when there’s no apparent logic behind which warehouse should fulfill which order. Consequences include:
- Fulfillment from distant warehouses despite closer options
- Higher shipping costs
- Longer delivery times
Misdirected orders can damage customer satisfaction and strain logistics budgets.
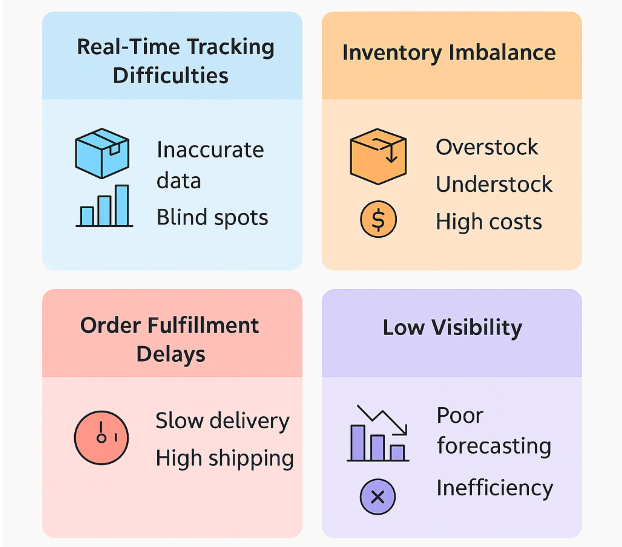
4. Low Visibility Across the Network
When warehouses operate in silos, managers can’t access consolidated inventory reports or performance metrics. This fragmented view leads to the following:
- Inconsistent replenishment cycles
- Inability to forecast accurately
- Inefficient use of resources
WMS Solutions for Efficient Multi-Warehouse Management
A. Centralized Inventory Control
A WMS unifies all warehouse data into one dashboard, offering real-time access to:
- Inventory levels by location
- Incoming and outgoing stock
- Historical usage patterns
Benefits:
- Minimize errors in data entry
- Improve forecasting and stock allocation
- Reduce unnecessary transfers
B. Standardized & Streamlined Processes
A WMS enforces consistency across warehouse tasks such as:
- Receiving and labeling
- Put-away strategies
- Picking and packing workflows
- Shipping protocols
Outcome:
- Higher accuracy in order fulfillment
- Easier cross-training of staff
- Faster onboarding in new warehouses
For example, e-commerce retailers like Gymshark and Allbirds implement standardized WMS processes to manage global fulfillment from regional hubs.
C. Optimized Order Management
Modern WMS solutions use automation and rules-based logic to route orders smartly.
- Brilliant warehouse selection based on proximity, stock levels, and shipping rates
- Dynamic reorder alerts to prevent stockouts
- Integration with ERP and e-commerce systems (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento)
This level of automation boosts fulfillment speed and customer satisfaction.

D. Advanced Data Tracking Technologies
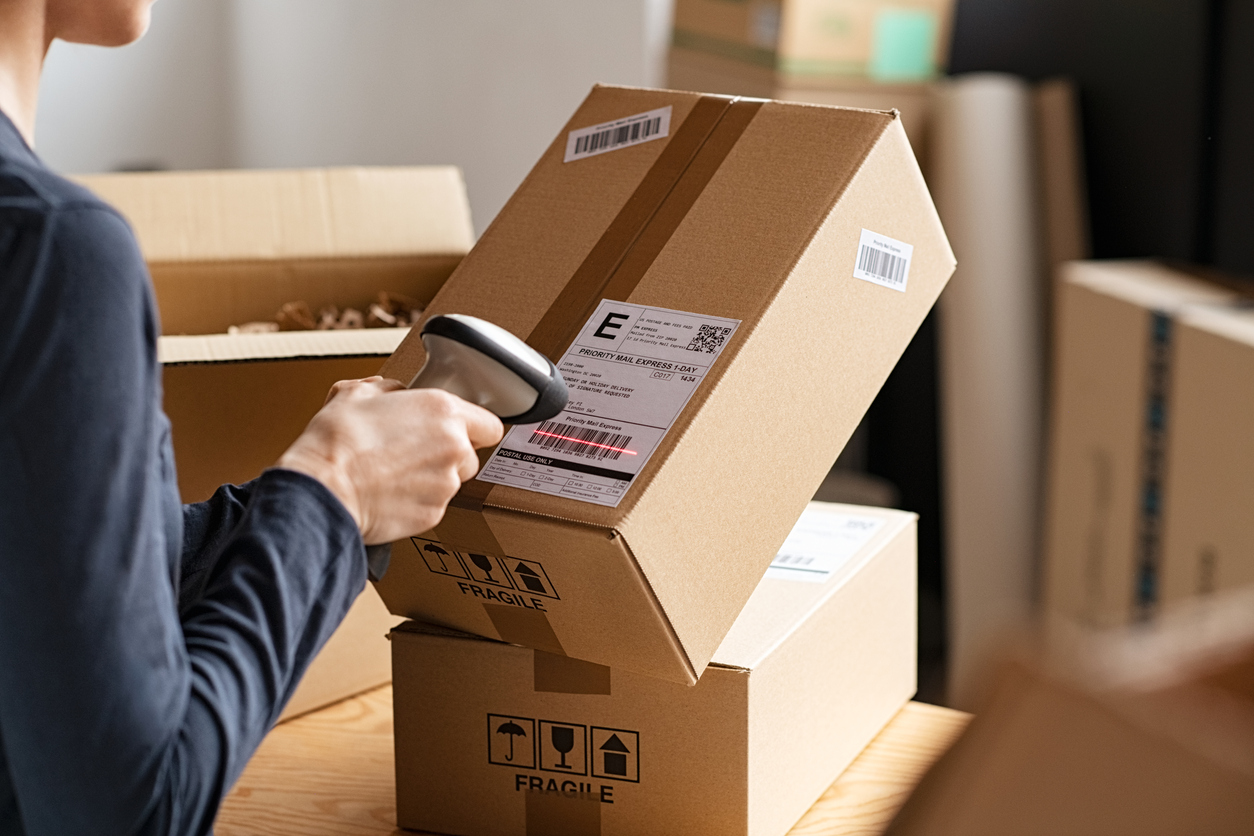
1. Barcode Scanning
- Ensures real-time updates during picking, receiving, and transfers
- Lowers error rates and manual workload
2. RFID Technology
- Enables real-time tracking of inventory movement across sites
- Applicable for high-value or fast-moving products
3. IoT Sensors
- Monitor temperature, humidity, or vibration for perishables and sensitive goods
- Enhance compliance with safety and quality standards
E. Clear Communication & Reporting
A WMS generates uniform reports that can be filtered by:
- Location
- Product category
- Time frame
- Order Status
Regular audits become easier, and inventory health metrics are always accessible.
Example: An apparel company can run weekly variance reports to identify shrinkage or miscounts by warehouse.
F. Digital Inventory Transfers
Manual transfers are time-consuming and error-prone. A WMS automates this process:
- Auto-generates transfer requests based on thresholds
- Tracks in-transit goods between facilities
- Reduces paperwork and miscommunication
This feature is beneficial for businesses that operate seasonal or pop-up fulfillment centers.
ROI Metrics to Expect from WMS Implementation
Businesses investing in multi-warehouse WMS often report:
- 20–30% reduction in inventory carrying costs
- 15–25% improvement in order accuracy
- Up to 40% faster order processing time
- Reduced labor costs due to automation
Case in point: A U.S.-based consumer electronics brand improved fulfillment time by 35% after integrating a cloud-based WMS across its four distribution centers.

Conclusion: Building a Scalable Warehouse Network with WMS
Managing inventory across multiple warehouses is no longer a manual, fragmented process. With the help of a modern WMS, businesses gain the tools to:
- Centralize inventory control
- Standardize operations
- Improve visibility and accountability
- Respond quickly to demand fluctuations
Looking Ahead: As technology evolves, AI-powered forecasting and advanced IoT integrations will further automate replenishment, demand planning, and environmental monitoring.
The Bottom Line:
Whether you run a regional fulfillment network or operate globally, a robust WMS is your foundation for accuracy, speed, and long-term scalability.
Data Source: Statista, “Warehouse Automation Market Size Worldwide (2023–2027)“
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua








[…] Connectivity: Seamless integration with WMS, OMS, and ERP […]
[…] Warehouse operations are critical to modern logistics, serving as the heart of supply chain management. Effectively managing warehouse functions is integral to the success of any logistics operation, as it directly impacts inventory levels, order fulfillment speed, and customer satisfaction. However, warehouse operations are facing increasing challenges, such as cost pressures, bottlenecks in efficiency, and a growing labor shortage. These challenges demand innovative solutions to optimize warehouse performance. […]
[…] can automatically select the most cost-effective option per order by comparing real-time shipping rates across carriers. This reduces overpaying for shipments and cuts down on reliance on default […]