How Technology Is Shaping Modern Trade Compliance Management
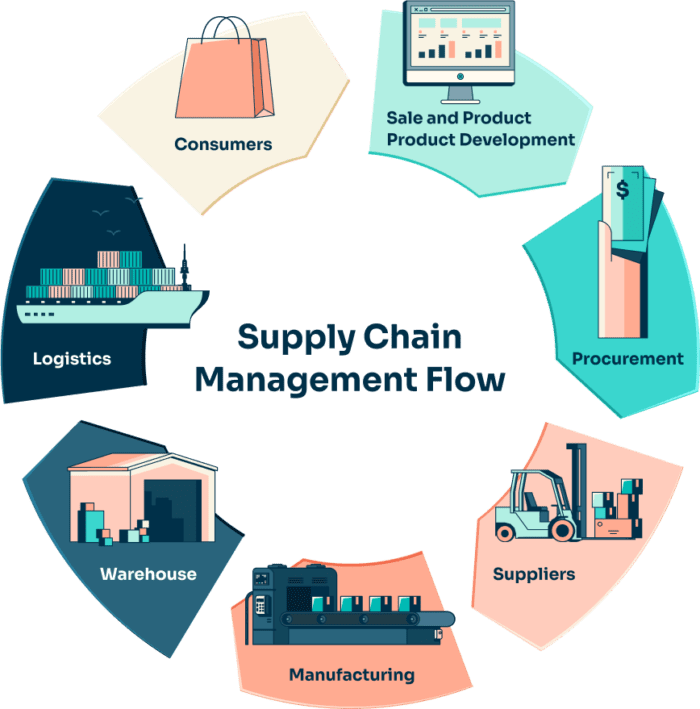
In today’s borderless economy, even small companies ship products across multiple jurisdictions. Each shipment must satisfy customs rules, export-control laws, and sanction regimes that change without notice. Failure can trigger fines, shipment delays, or a revoked license. Technology now sits at the center of effective trade compliance management, turning a once paper-heavy chore into a data-driven business process.
1. From Clipboards to Cloud Platforms
Two decades ago, compliance teams relied on printed tariff books, faxed invoices, and monthly CD-ROM updates. These static tools quickly became outdated. Cloud-based platforms now pull live regulatory data from customs authorities and integrate it directly into an ERP. The result is a single source of truth that lets managers run checks on every transaction in near-real time.
2. Automation Cuts Manual Labor
Modern compliance suites use rules engines and AI classifiers to automate routine decisions:
- HS/ECCN classification: Natural-language processing reads product specs and suggests tariff codes.
- Restricted-party screening: APIs compare each customer and supplier against updated sanction lists.
- License determination: Decision trees validate whether an export license is required before an order is released.
Automating these steps reduces human error, speeds order fulfillment, and frees specialists to handle strategic issues rather than repetitive tasks. It also embeds trade compliance controls directly into the order-to-cash workflow, so violations are stopped before goods leave the warehouse.
3. Real-Time Dashboards Expose Hidden Risk
Static spreadsheets only show yesterday’s exceptions. By contrast, cloud dashboards stream data from logistics partners, brokers, and government portals. Compliance officers can:
- Track shipment status across ports, airports, and borders.
- See risk scores that highlight unusual destinations or sudden volume spikes.
- Drill into a transaction’s full audit trail with two clicks.
Immediate insight lets a team correct course fast—rerouting a container, requesting a missing certificate, or placing a temporary hold until a license is approved.

4. Data Analytics Drive Continuous Improvement
Raw data without analysis is just noise. The newest trade compliance management tools apply machine-learning models to detect patterns:
- Products are repeatedly misclassified in certain regions.
- Suppliers whose paperwork often triggers customs holds.
- Routes where dwell time exceeds the norm.
When teams act on these findings—by updating product databases, training suppliers, or choosing faster lanes—clearance times fall and penalty exposure shrinks.
5. Integration Eliminates Silos
A compliance system adds the most value when it talks to everything else:
| System Connected | Benefit for Compliance |
|---|---|
| ERP | Shares master data, pricing, and Incoterms |
| Warehouse & TMS | Adds SKU weight, origin, and routing info |
| Broker Portal | Automates document filing and status feeds |
| Government API | Receives live rulings and regulatory updates |
Seamless integration means a shipment record never needs re-keying, lowering both cost and error rates.
6. Blockchain Raises Trust and Traceability
Early adopters are piloting blockchain networks to store bills of lading, certificates of origin, and inspection records. Because every participant sees the same tamper-proof ledger, disputes over document integrity vanish. Auditors gain instant proof, while counterfeit and diversion risks drop.
7. Mobile Apps Keep Field Teams Connected
Not all compliance decisions happen at a desk. Mobile applications allow inspectors and warehouse staff to:
- Scan a barcode to view license status.
- Capture photos of damaged seals for the audit file.
- Receive push alerts when a shipment requires additional screening.
Putting information in an employee’s hands at the loading dock closes the loop between policy and execution.
8. Artificial Intelligence Learns and Adapts
AI is more than a buzzword. Predictive engines now crunch millions of historical entries to forecast which new orders might trigger customs reviews. Each outcome—released, inspected, or detained—feeds back into the model, sharpening its accuracy over time. This learning loop turns trade compliance from reactive policing into proactive prevention.
9. Measuring Return on Technology
Investments still require justification. Firms track metrics such as:
- Average clearance time per shipment.
- Number of manual classification overrides.
- Annual fines or audit findings.
- Staff hours saved by robotic process automation.
Companies that deploy end-to-end trade compliance management platforms often report clearance time reductions of 30% and penalty cuts of 50% within the first year.
10. Building a Future-Proof Compliance Program
Technology alone does not guarantee success. Leaders should:
- Align tools with clear governance policies and executive sponsorship.
- Train staff continuously—regulations and software both evolve.
- Maintain clean, complete master data; faulty inputs ruin the best algorithm.
- Review system rules quarterly to reflect new tariff schedules and sanctions.
A balanced focus on people, process, and platform ensures sustainable results.
Conclusion
Technology has transformed modern trade compliance management from a reactive, paper-bound function into a strategic capability. Automation speeds mundane tasks, real-time visibility exposes risk, and analytics deliver insight for continuous improvement. As global regulations tighten and supply chains stretch, businesses that embrace these digital tools will avoid costly violations, accelerate shipments, and gain a competitive edge in international markets.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua