Blockchain in Smart Logistics for Transparency
In today’s global economy, supply chains stretch across countries and involve many different partners. This makes it harder than ever to keep track of goods and build trust. Traditional logistics systems often lack clear visibility, making it difficult to monitor shipments in real time, confirm product authenticity, or spot problems like delays and fraud. That’s where smart logistics and blockchain come in—two powerful technologies that are changing how companies manage and protect their supply chains.
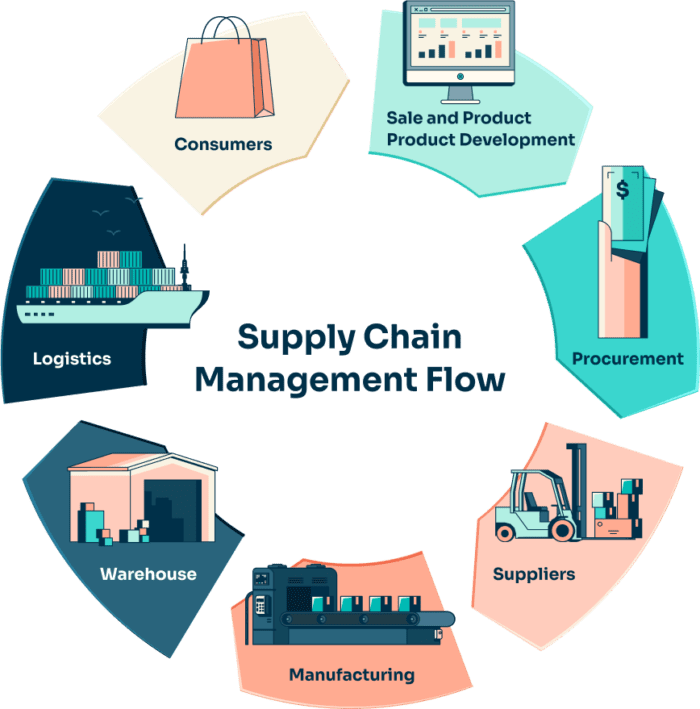
I. What Is Smart Logistics?

Smart logistics refers to the use of advanced digital technologies—such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, big data, and automation—to optimize and streamline logistics and supply chain operations. The goal is to make logistics systems more intelligent, adaptive, and responsive.
Key components of smart logistics include:
- Real-time tracking systems using GPS and IoT sensors
- Predictive analytics to forecast demand, traffic, and delays
- Automated warehouse management and robotic fulfillment
- AI-driven route optimization and fleet management
These tools help companies reduce costs, speed up delivery times, and improve customer satisfaction. But while smart logistics solves many operational challenges, it still relies on centralized databases and trust between multiple parties—an area where blockchain technology becomes essential.
II. The Transparency Problem in Traditional Supply Chains
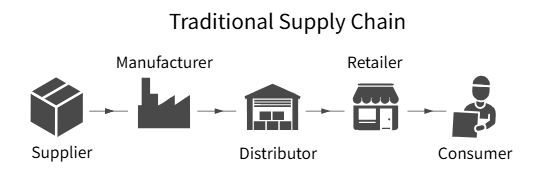
Even with technological upgrades, most supply chains still suffer from a lack of end-to-end visibility. Data is fragmented across systems and controlled by individual organizations. This lack of transparency leads to several problems:
- Delayed or missing information
- Inaccurate inventory or shipment data
- Counterfeit products entering the supply chain
- Difficulties in tracing the origin of goods
- Regulatory compliance issues
These risks can be especially damaging in sensitive industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods.
III. Blockchain: A Solution for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that enables multiple parties to record transactions in a secure, verifiable, and transparent manner. Once data is recorded in a blockchain, it cannot be altered without the agreement of all involved parties.
Here’s how blockchain transforms supply chain transparency:
1. Decentralized Record-Keeping
Instead of relying on a single centralized system, blockchain allows each stakeholder (supplier, manufacturer, distributor, retailer, and customer) to access a shared and synchronized database. This ensures that everyone sees the same version of the truth.
2. Traceability and Provenance
Blockchain provides an unbroken chain of custody from raw material to end user. Every touchpoint—harvest, production, shipping, customs, warehousing, retail—is time-stamped and recorded, allowing complete traceability.
3. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are programmable agreements that automatically execute once pre-defined conditions are met. For example, a payment can be automatically triggered once a delivery is confirmed by GPS data—reducing delays and administrative costs.
4. Fraud Prevention
Blockchain’s immutability makes it virtually impossible to manipulate records without detection. This protects against fraud, theft, and counterfeiting.
IV. Real-World Use Cases

Major companies and industries are already integrating blockchain into their logistics processes:
- Walmart uses blockchain to trace the source of food products within seconds, enhancing food safety and recall efficiency.
- IBM and Maersk developed TradeLens, a blockchain platform used to manage and track shipping containers across global ports.
- Pharmaceutical companies are using blockchain to comply with regulations like the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), ensuring that medicines are genuine and properly handled.
- Fashion and luxury brands use blockchain to prove authenticity and ethical sourcing.
These real-world applications show how blockchain and smart logistics can work together to increase accountability, trust, and operational efficiency.
V. Benefits of Combining Smart Logistics and Blockchain

When integrated, smart logistics and blockchain deliver a number of powerful benefits:
- Full transparency from start to finish
- Real-time visibility into inventory and shipments
- Reduced paperwork and manual errors
- Lower operational and compliance costs
- Greater consumer trust through verified product history
- Faster response to recalls, disruptions, or disputes
This powerful combination not only improves operational agility but also enhances corporate social responsibility by enabling ethical sourcing, sustainability tracking, and compliance monitoring.
VI. Challenges to Adoption
Despite the benefits, there are hurdles to implementing blockchain in smart logistics:
- High setup and integration costs
- Complexity of integrating with legacy systems
- Lack of industry-wide standards and interoperability
- Scalability issues in public blockchains
- Need for skilled personnel and training
However, as technology matures and blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms become more accessible, these barriers are gradually diminishing.
VII. The Future of Transparent Supply Chains

Looking ahead, the convergence of smart logistics and blockchain will likely become standard in global supply chains. Governments and regulators are also encouraging greater transparency, and customers increasingly demand to know the origin, sustainability, and ethics behind the products they buy.
Emerging trends to watch include:
- Integration with AI and IoT for predictive and autonomous supply chains
- Digital twins of supply chain assets, recorded on blockchain
- Greater use of tokenization and decentralized finance (DeFi) in logistics contracts
In the evolving landscape of global trade, visibility and trust are essential. Smart logistics and blockchain offer a powerful, future-ready combination to solve the long-standing issues of opacity and inefficiency in supply chains. Companies that embrace these technologies not only gain a competitive advantage but also position themselves as leaders in transparency, sustainability, and innovation.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua