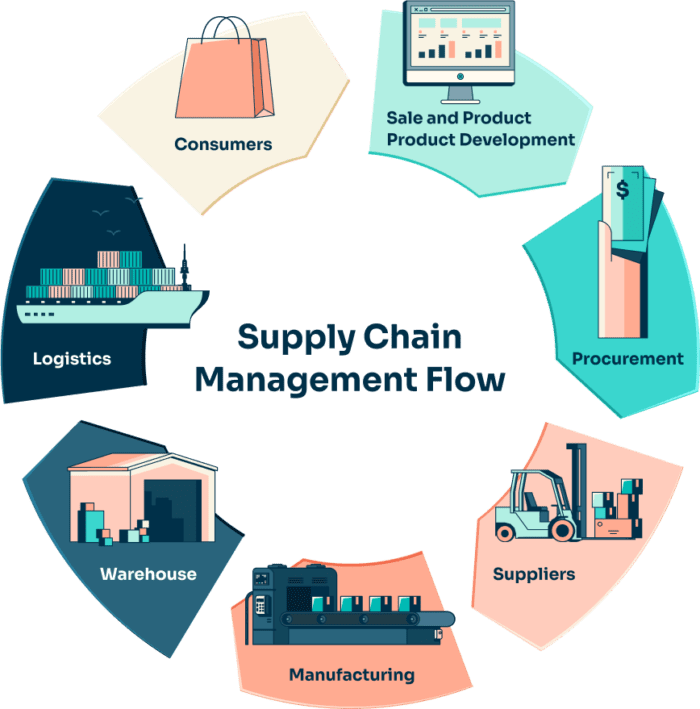
How to Decode a GS1-128 Barcode on Shipping Labels
GS1-128 barcodes are essential tools in logistics, providing a standardized way to track and manage shipping and product information. Used on shipping labels, these barcodes encode critical data like product numbers, batch details, and shipping information. In this article, we’ll break down how to read and decode a barcode, focusing on the essential elements of these labels for easy interpretation.
What is a GS1-128 Barcode?
A GS1-128 barcode is part of the GS1 system, designed to handle complex data requirements in shipping, warehousing, and product tracking. Based on the Code 128 format, it can store multiple types of data, such as serial numbers, expiration dates, and lot numbers, along with an application identifier (AI) that specifies the type of data being encoded. This barcode allows businesses to streamline logistics, improve accuracy, and meet regulatory requirements, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
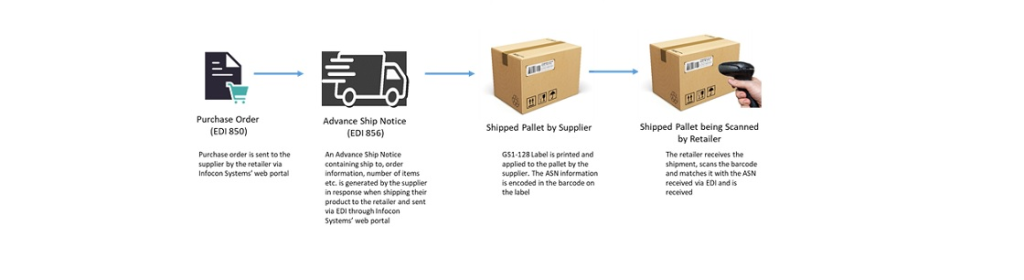
Decoding the GS1-128 Barcode
To effectively decode a GS1-128 barcode, it’s crucial to understand its components. A barcode typically includes:
- Start/Stop Characters: These indicate the beginning and end of the barcode.
- Data Characters: The encoded information, including numbers and letters.
- Application Identifiers (AIs): These identifiers define what the data represents (e.g., a serial number or expiration date).
- Check Digit: A value used to verify the accuracy of the barcode’s data.
The data within the barcode is organized in a standardized way to allow businesses to efficiently process and manage shipments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Decoding a GS1-128 Barcode
1. Scan the Barcode
Use a barcode scanner to read the GS1-128 barcode. Most modern barcode scanners support that, and once scanned, the encoded data is transmitted to a connected system, such as a computer or mobile device.
2. Identify the Application Identifiers (AIs)
Application Identifiers (AIs) are key to understanding the meaning of the data encoded in the barcode. Each AI is associated with a specific type of data:
- (01) typically represents a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN).
- (10) may indicate a batch or lot number.
- (17) could refer to an expiration date.

Recognizing these AIs helps you determine how to interpret the data that follows them.
3. Decode the Data
After identifying the AIs, look at the associated data. The content following each AI is typically numeric or alphanumeric and should be interpreted according to the AI’s specification. For example, if the AI is (01), it’s likely encoding a GTIN, which is a product’s unique identifier.
4. Verify the Check Digit
To ensure the barcode has been scanned correctly, check the check digit. This digit is calculated using a specific formula based on the other digits in the barcode. Barcode scanners usually verify this automatically, but it can be manually checked if needed.
5. Use the Decoded Data
Once decoded and verified, the data can be used for its intended purpose. For instance, the GTIN can be used to search for product details in an inventory system, while a batch number could track a product through manufacturing and shipping.

Common Applications of GS1-128 Barcodes
GS1-128 barcodes are used in a wide range of industries to improve supply chain management. Some key applications include:
- Shipment Tracking: It helps monitor shipments by encoding tracking numbers, lot information, and product details.
- Inventory Management: By decoding these barcodes, businesses can track inventory levels, reorder stock, and streamline their warehouse operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: In regulated industries like pharmaceuticals and food, the barcodes are used to encode critical information like expiration dates and lot numbers, helping companies meet legal requirements.
- Error Reduction: Barcode scanning eliminates manual data entry errors, ensuring accurate product and shipment information.
How GS1-128 Barcodes Benefit Businesses
The ability to read and decode barcodes brings numerous benefits to businesses involved in logistics and inventory management:
- Improved Efficiency: Barcodes streamline data collection and processing, reducing delays in shipping and inventory checks.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Automated scanning minimizes human error and ensures that product information is correctly captured.
- Regulatory Adherence: It supports compliance with industry regulations by ensuring critical product and shipping details are encoded on labels.
- Better Visibility: With precise tracking and data management, businesses gain better control over their supply chains, from manufacturing to delivery.
Conclusion
GS1-128 barcodes are essential tools for efficient product tracking and shipping management. By understanding how to decode these barcodes, businesses can improve accuracy, streamline operations, and ensure regulatory compliance. Mastering barcode decoding is a key step towards optimizing supply chain processes and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua