Essential Guide to Combining IoT and GPS Tracking for Smarter Freight Management
The freight and transportation industry faces constant pressure to deliver goods faster, safer, and more cost-effectively. To meet these demands, businesses use technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and GPS tracking to improve traditional freight management systems.
This article explains how integrating IoT with GPS tracking benefits freight operations by enhancing visibility, improving security, reducing costs, and enabling better decision-making throughout the supply chain.

1. Understanding IoT in Freight Management
IoT refers to a network of connected physical devices with sensors, software, and network capabilities. In freight management, these devices are often attached to:
- Shipping containers
- Pallets or individual packages
- Trucks and delivery vehicles
- Warehouses
IoT sensors monitor various data points such as temperature, humidity, vibration, shock, door activity, and fuel usage. This information allows logistics managers to track both the location and condition of cargo during transit.
2. The Role of GPS Tracking in Logistics
GPS tracking delivers real-time location data for vehicles and shipments. While GPS alone can show vehicle routes and delivery progress, combining it with IoT creates a complete view of freight status.
GPS is commonly used to:
- Optimize delivery routes
- Monitor driver behavior
- Improve delivery accuracy
- Deter theft
Logistics companies can detect delays, monitor travel patterns, and improve on-time delivery performance by tracking vehicle movement in real time.
3. The Power of Integration: IoT + GPS
Merging IoT and GPS provides a powerful data-driven solution. This combination supports more innovative freight management in several ways.
a. Real-Time Visibility Across the Supply Chain
IoT and GPS together offer live updates on freight location and condition. Shippers, warehouse operators, and customers can all view status information as shipments move along the route.
For example, if a refrigerated shipment experiences a temperature increase, the system can send a real-time alert, helping prevent product spoilage.
b. Enhanced Security and Theft Prevention
Cargo theft remains a concern in logistics. GPS enables real-time vehicle location tracking. IoT sensors add another layer of security by detecting door tampering or unplanned route changes. Some systems can even trigger alarms or block engine ignition when suspicious activity is detected.
c. Improved Asset Utilization and Efficiency
IoT and GPS help monitor idle trucks, loading dock time, and route efficiency. Fleet managers can improve scheduling, avoid delays, and reduce unnecessary fuel consumption.
This leads to more effective use of vehicles and labor.
d. Automated Documentation and Compliance
Industries such as food and pharmaceuticals often require proof that goods were transported under specific conditions. IoT sensors can record temperature, movement, and shock data throughout the journey. Combined with GPS logs, this creates a complete audit trail for regulatory or client review.

e. Predictive Maintenance and Fleet Monitoring
IoT sensors collect engine data, tire pressure, and battery performance. When this data is paired with GPS location, maintenance can be planned. Vehicles get serviced before breakdowns occur, keeping deliveries on schedule.
4. Real-World Use Cases
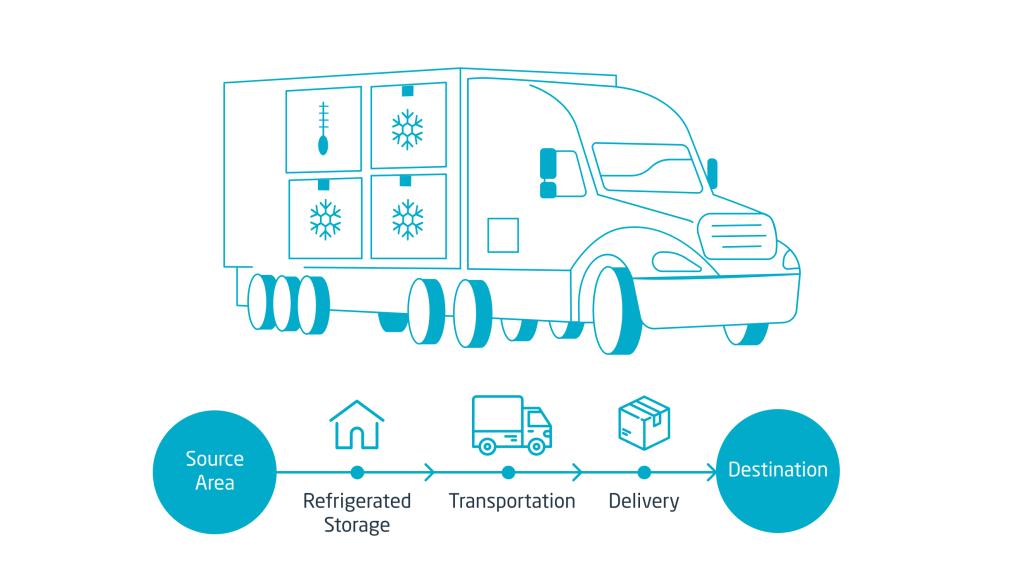
Cold Chain Logistics
Perishable goods like vaccines, seafood, and dairy require constant refrigeration. IoT monitors temperature and humidity, while GPS ensures route tracking and delivery timing. Alerts help teams act fast if conditions change during transit.
High-Value Cargo
Items like electronics or luxury goods face a higher risk of theft. IoT sensors detect tampering or shock events. GPS allows companies to locate shipments and take action quickly.
Large-Scale Fleet Operations
Enterprises with large truck fleets benefit from complete visibility over all routes and vehicle statuses. Real-time data supports dispatch decisions, route changes, and fuel optimization.
5. Implementation Considerations
Before deploying these technologies, a few factors should be addressed:
- Data management: IoT and GPS generate large amounts of data. A reliable system must be in place to store and analyze it.
- Device compatibility: Sensors and trackers from different vendors must work smoothly together.
- Durability and power: Devices should operate in harsh environments and for extended periods.
- Cybersecurity: To prevent data leaks or unauthorized access, networks and devices must be protected.

- Budget planning: Initial costs can be high, but efficiency improvements often lead to savings.
6. The Future of Freight Tracking
The next step in freight tracking includes combining IoT and GPS with artificial intelligence and machine learning. These tools can help predict delays, suggest route changes, and even automate dispatch decisions.
Autonomous vehicles, drones, and innovativewarehousing solutions are also beginning to incorporate GPS and IoT for better control and coordination.
Conclusion
Integrating IoT and GPS tracking enables smarter, faster, and safer freight operations. This combination delivers real-time visibility, improves asset control, and boosts service quality.
Companies that embrace this technology can respond to challenges with greater agility and improve operational performance. As transportation networks become more complex, intelligent freight tracking plays an increasingly important role in keeping goods moving efficiently and securely.
Industry Insights
news via inbox
Nulla turp dis cursus. Integer liberos euismod pretium faucibua